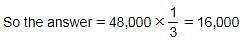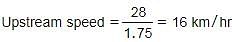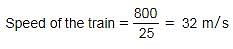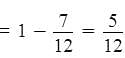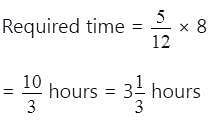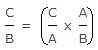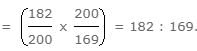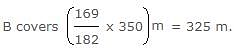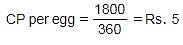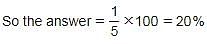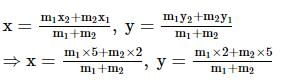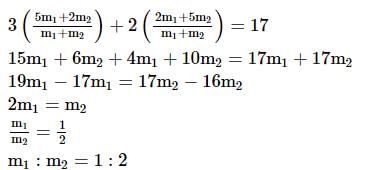Indian Coast Guard Navik GD Mock Test - 8 - Indian Coast Guard Navik GD/DB MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Indian Coast Guard Navik GD Mock Test Series 2024 - Indian Coast Guard Navik GD Mock Test - 8
For the arrangements of the letters of the word INDIA, how many words would start with the letter I?
39 persons can repair a road in 12 days, working 5 hours a day. In how many days will 30 persons, working 6 hours a day, complete the work?
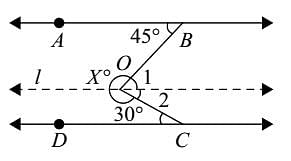
In the given, AB || CD. Then X is equal to:
A person deposited Rs. 48000 at 10% p.a. simple interest for 2 years and Rs. X at 10% p.a. simple interest for 4 years. If his overall interest is 25% of the overall amount, what is the value of X?
A bet was placed between two friend ram and shyam to find out what will be the chance that a leap year selected at random contains 53 Fridays?
The still water speed of a boat is 30 km/hr. It goes 28 km upstream in 1 hour 45 minutes. What is the downstream speed of the boat?
If an 800 meters long train crosses a pole in 25 seconds, what is the speed of the train?
Pipe A can fill an empty tank in 6 hours and pipe B in 8 hours. If both the pipes are opened and after 2 hours pipe. A is closed, how much time B will take to fill the remaining tank?
In a race of 200 m, A can beat B by 31 m and C by 18 m. In a race of 350 m, C will beat B by:
A and B invested Rs 20000 and Rs 30000 respectively and agreed to share profit in the ratio of their capitals. C entered into the partnership with the condition that profit would be divided between A, B and C in the ratio 3 : 4 : 3 for which he paid Rs 50000 as premium; in what ratio would the premium be divided among A and B?
A shopkeeper bought 360 eggs for Rs. 1800. If he sold all the eggs for Rs. 6 each, what is his overall profit/loss percentage?
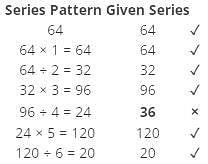
Directions: Find the wrong term in the given series.
64 64 32 96 36 120 20
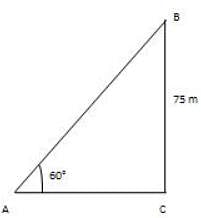
A kite is flying at a tallness of 75 m from the level of ground, joined to a string slanted at 60° to the level. The string's length is:
A printer takes 0.012 seconds to print one alphabet. How long will he take to print the word ‘mathematics’?
There are 6 pink and 4 white balls in a bag. If two balls are drawn from the bag, what is the probability that both the balls are white?
A flagstaff 17.5 meters high casts a shadow of length 40.25 meters. What will be the height of a building, which casts a shadow of length 28.75 meters under similar conditions?
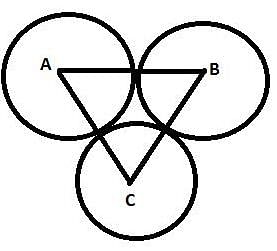
The three equal circles touches each other externally. If the centres of these circles be A, B, C then ΔABC is ________
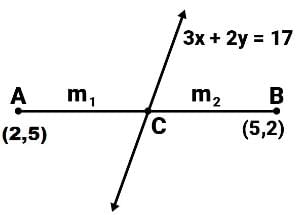
Find the ratio in which line 3x + 2y = 17 divides the line segment joined by points (2,5) and (5,2).
The conversion factor to convert miles to kilometers is approximately
Which of the following is an example of an exothermic reaction?
The correct electronic configuration of sodium is:
Which element is located at the bottom right corner of the periodic table?
Which one has the maximum number of unpaired electrons?
What is the substance that is oxidized in a redox reaction known as?
What is the common name for ethanoic acid?