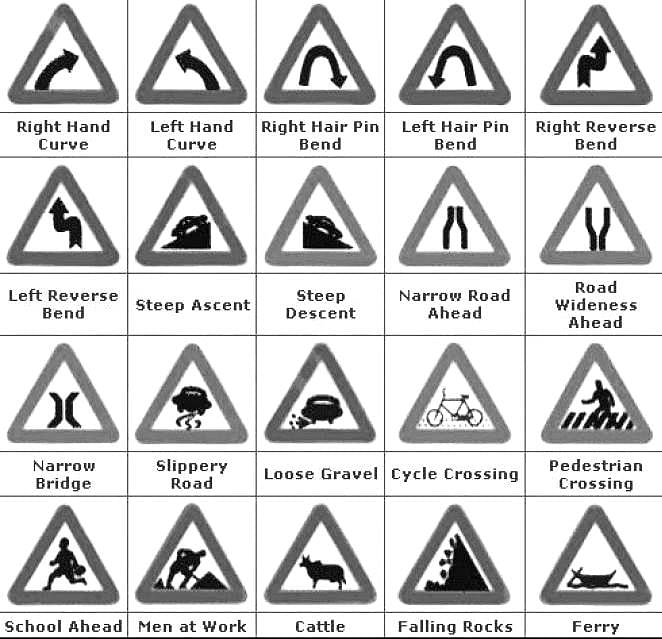
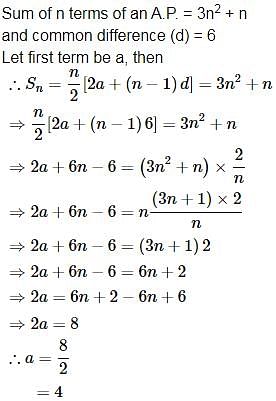HSSC TGT Math Mock Test - 5 - HSSC PGT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test HSSC TGT Mock Test Series 2024 - HSSC TGT Math Mock Test - 5
Identify environmental issues which are local in nature:
(i) Depletion of ozone layer
(ii) Lake pollution
(iii) Soil erosion
(iv) Climate change
(v) Water logging
(vi) Solid Waste Management
Select the answer from the options given below:
Which of the following are not the major cause of biodiversity loss in a geographical region?
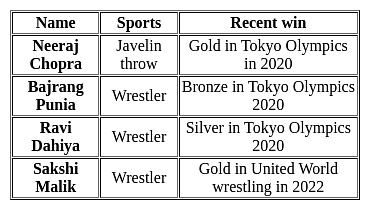
Who was honoured with the title 'Rai Bahadur' in Haryana?
In this year the campaign of Beti Bachao Beti Padhao was started in Haryana.
These are the methods of water conservation, identity which of these are the right process for conservation -
1. Using drip irrigation by farmers.
2. Rainwater is collected by pipes and stored in tanks.
3. Using more water to clean the toilets and washrooms.
4. Water saving habits are introduced to small children.
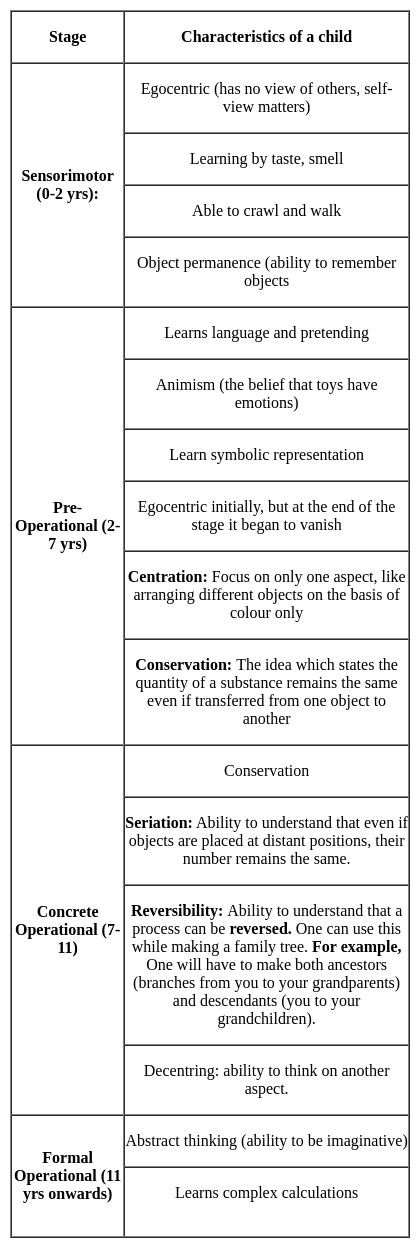
To understand the relationships among relatives on a family tree, children need to be able to use the skill of:
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason just below it. Of the statements, mark the correct answer as
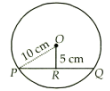
Assertion : The length of a chord which is at a distance of 5 cm from the centre of a circle of radius 10 cm is 17.32 cm.
Reason : The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
The equations, x + 4 y – 2 z = 3, 3 x + y + 5 z = 7, 2 x + 3y +z = 5 have
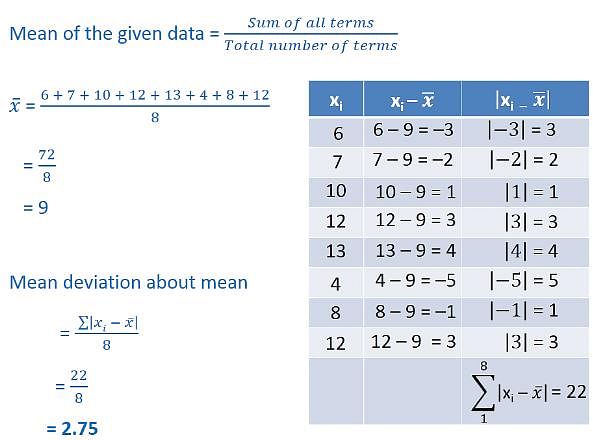
The mean deviation about the mean for the following data: 6, 7, 10, 12, 13, 4, 8, 12.
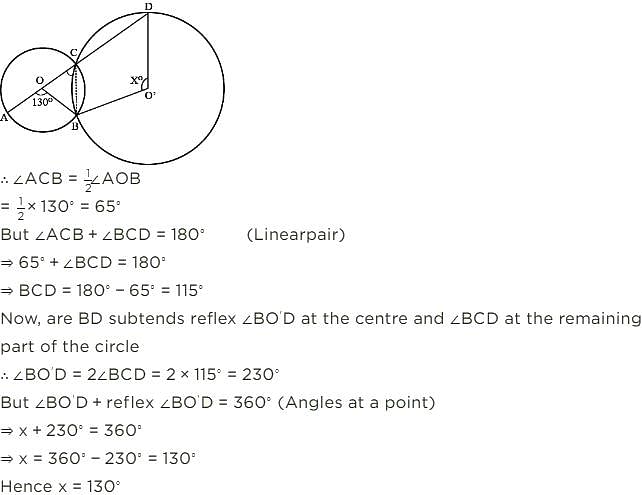
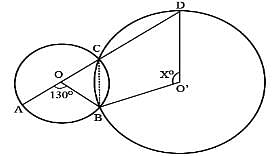
In the figure, O and O' are centres of two circles intersecting at B aand C. ACD is a straight line, find x.
The perpendicular distance of a point Q(4, 7) from y-axis is
If A any square matrix then which of the following is not symmetric ?
If the sum of first n terms of an AP be 3n2 + n and it's common difference is 6, then its first term is :
Show that the points A(1, – 2, – 8), B (5, 0, – 2) and C (11, 3, 7) are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides AC.