TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 6 (Geography) - TS TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test TS SET Mock Test Series 2024 - TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 6 (Geography)
Which of the following periods is referred to as a period of stagnant or stationary phase of growth of India’s population?
Which of the following model is an example of spatial interaction?
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct answer using the code given below.
Assertion (A) : Central Business District (CBD) of a city has high concentration of wholesale stores, offices and cultural and recreational activities.
Reason (R) : Prices and demand of real increases as distance towards CBD reduces.
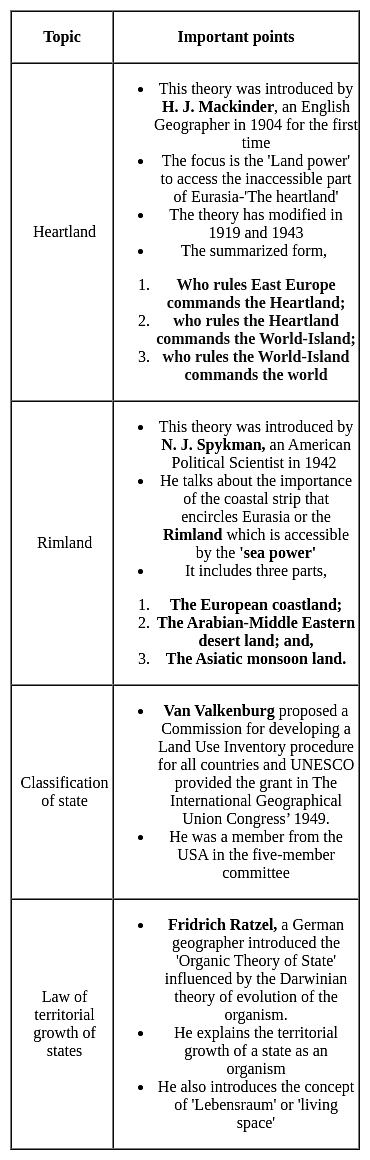
Match List I with List II:
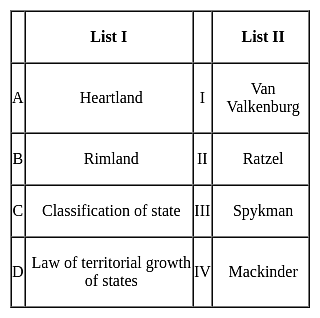
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
____________ predominantly acts as the agent of chemical erosion of soil.
Which of the following is NOT a use of total station?
Consider the following statements regarding the transport sector:
1. The value of the material is significantly enhanced by transportation.
2. In selecting the mode of transport, distance, in terms of time or cost, is the determining factor.
3. Isochrone lines are drawn on a map to join places equal in terms of the time taken to reach them.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?Brahmaputra River when it flows out of India into Bangladesh is called as ________?
What is the significance of understanding landscape evolution according to the passage?
What criticism has the cycle of erosion theory faced?
In which stage of landscape evolution do relief features become more subdued?
What is the primary driving force behind the cycle of erosion theory?
Sub tropical high-pressure belt is called ………………
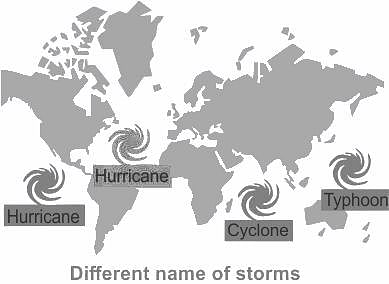
A cyclone is known by different names in different parts of the world. In Philippines it is called as _______.
Read the following statements about sustainable development.
Statement (A): Sustainable development is a process of maximum exploitation of resources.
Statement (B): In absence of sustainable development non-renewable resources can definitely get exhauste.
Choose the correct option.
Identify the option that arranges the following states' literacy rates in descending order, according to Census 2011.
A. Kerala
B. Himachal Pradesh
C. Haryana
Compared with North American cities, western European cities are generally more compact, with lower skylines, narrower streets, and more irregular street patterns. This difference is primarily a reflection of the:
|
60 tests
|