KTET Paper 2: Child Development and Pedagogy Test - 1 (Social Science) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test KTET Mock Test Series 2024 - KTET Paper 2: Child Development and Pedagogy Test - 1 (Social Science)
'Special needs education' is the type of education
Assertion (A): Reflex actions such as sucking, grasping inherited by the adults become the building blocks for cognitive learning during pre-logical stage.
Reasoning (R): Piaget believed that adults are active learners who are responsive to stimulation in their environment.
Reasoning (R): Piaget believed that adults are active learners who are responsive to stimulation in their environment.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A child 'who is in the middle of his school (about ten and half years) is unable to do the work of the class below that which is normal for his age" is known as which types of children?
Learning outcome depends upon which of the following?
What is the primary difference between Piaget's and Vygotsky's theories of language development?
A teacher wants her students to know about government schemes through primary sources. Which one of the following schemes is inappropriate?
Case-history method is more effective to study which of the following problem behaviours of a child?
Anupama, a science teacher, often makes linkages in her classrooms with the concepts students are studying in Mathematics. This kind of pedagogy -
The theory of classical conditioning was propounded by I.V. Paulov in the year _______________.
For which of the following trial and error method is more useful?
In the following two sets of information, Set-I mentions the stages of cognitive development as given by Piaget and Set-II specified the distinctive cognitive features:
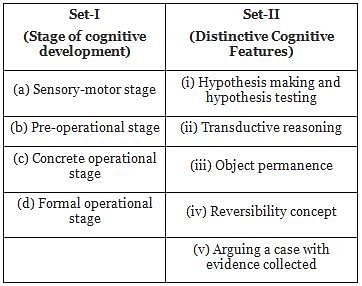
Match the two sets and indicate your answer from the options given below:
Children in _______ stage have symbolic thinking but do not realize that actions can be reversed and their judgments are based on the immediate appearance of things.
"The curriculum must enable children to find their voices, nurture their curiosity—to do things, to ask questions and to pursue investigations, sharing and integrating their experiences with school knowledge—rather than their ability to reproduce textual knowledge." (National Curriculum Framework 2005, pg-13)
Against this backdrop, what should be the primary role of a teacher?
According to Piaget, which period among the following is the "period of concrete operations"?
IQ level of extraordinary students lies between:
Karnail Singh does not pay income tax despite legal procedures and expenses. He thinks that he cannot support a corrupt government which spends millions of rupees in building unnecessary dams. He is probably in which state of Kohlberg's stages of moral development?
Which one of the following group of characteristics is not related to creative thinking?
During classroom discussions, a teacher often pays more attention to boys than girls. This is an example of:
Determinants of individual differences in human beings relate to which of the following?
Which of the following are criticisms of Kohlberg's theory?
A. Kohlberg proposed a theory without taking gender differences into consideration
B. Kolberg proposed that moral reasoning is developmental
C. Kohlberg did not account for cultural differences in moral reasoning
D. Kohlberg give six clear cut stage of moral development in three levels
______ exhibits a basic level of order, but the teacher still struggles to maintain it.
By placing students in the least restricted school environment, the school
Errors made by children are indicative of-
_________ aims to study a child's development, especially information processing, conceptual processing, perceptual skills, language learning and other aspects related to brain development.
Achievement motivation is
What is the structure of school education as recommended by the National Education Policy 2020?
(i) 5 + 3 + 3 + 4
(ii) 2 + 3 + 3 + 4
(iii) 2 + 5 + 3 + 2 + 2
(iv) 5 + 3 + 3 + 2 + 2
Which kind of assessment ‘Sums-up’ how much a student has learned over a period of time?
Which of the following is properly sequenced in the context of motivation cycle?
Which of the following are strategies to increase the motivation level of the learners?
I. Build strength first
II. Propose alternatives
III. Facilitating creativity
IV. Providing a safe environment
Child development emphasis on:
|
100 tests
|

















