KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 6 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test KTET Mock Test Series 2024 - KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 6
Which option is true regarding the mistakes made by the student during the learning of mathematics at the elementary school level?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, then focal length of lens will be:
The value of a machine depreciates at the rate of 10% per year. It was purchased three years ago. If its present value is Rs. 1,45,800, then for how much was it purchased?
The total number of peripheral nerves in a human being is
Two organisms are best friends and live together. One provides shelter, water and nutrients while the other prepares and provides food. Such an association of organisms is termed as
A chord 70 cm long is drawn in a circle of diameter 74 cm. The perpendicular distance of the chord from the center is (in cm) :
The bile juice secreted by the liver and stored in the gall bladder, mainly helps in the breakdown of ______.
Which among the following is a natural indicator?
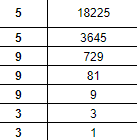
The internal base of a rectangular box is 15 cm long and 12(1/2)cm wide and its height is 7(1/2)cm. The box is filled with cubes, each of side 2(1/2)cm. The number of cubes will be
Examine the following:
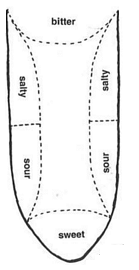
(A) The tip of the tongue - sweet taste
(B) The back of the tongue - sour taste
(C) The edges of the tongue - bitter taste
(D) The middle of the tongue - salty taste
Which of the above given pairs is correct?
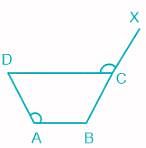
In the quadrilateral ABCD shown above, ∠DAB = ∠ DCX = 120°. If ∠ABC = 105°, what is ∠ADC equal to?
Which is the largest gland in our body that is characterised by its reddish brown colour?
Select the plants which do not have roots, stems, and leaves.
The bone bends but does not break in children. This is usually called
A body in uniform motion in one dimension moves from a position X1 at time t1 to another position X2 at time t2. Which of the following statements is wrong for this motion?
To be a “good” mathematician one must be able to
The subject which is most suitable to develop reasoning power of students is –
In Class VII, a teacher taught the 'properties of all types of quadrilaterals'. In the class test that followed after the unit, the teacher asked the problems on construction of quadrilateral. No one in the class was able to perform in the test. The reason may be
Which of the following is the most important stage in diagnosis?
Lesson planning in Life Sciences should be guided primarily by the consideration of
“Mathematics helps to develops qualities of cleanliness, punctuality, honesty, self-confidence” this statement related to which type of mathematical values.
Which of the following is the weakest force?
The teacher demonstrates an experiment to the students to show that Water boils at low temperature under low pressure. He takes the flask and fills it half with the water. Boils the water, and remove the flame. Closes flask and inverts it and pour cold water on the flask. The students observe the process carefully and see that water has begun to boil again when cold water is poured on the bottom of the inverted flask. During the task students asked various questions like:
a) Why is the water boiling?
b) Why did the water boil first?
c) Why was the flask closed and then inverted?
d) Why was cold water poured over the bottom of the inverted flask?
e) Why did the water boil in the flask when cold water is poured over the inverted flask?
At which step of the scientific method do these students have?
When an odd number is multiplied with an odd number, the result is an odd number. To teach this fact, what method will you follow?
Errors/difficulties in learning Science are identified using
National Curriculum Framework (NCF) strongly recommends that Science education at upper primary stage should
|
100 tests
|