APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (Geography) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test APSET Mock Test Series 2025 - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (Geography)
The theory of plate tectonics proposes that the earth’s lithosphere is divided into ______ major and some minor plates.
The Negroid race is indigenous to which of the following continents?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Who in 1905 clearly expressed the logical arguments concerning the place of the Earth’s body in the field of Geography?
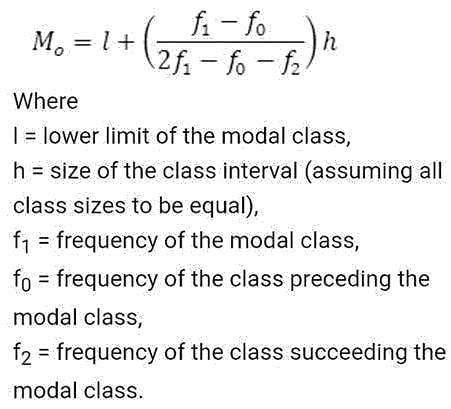
The histogram is the most useful to find the value of:
Which type of settlement pattern is having the following features?
1. narrow meandering streets and lanes
2. high population density
3. the high degree of nucleation
4. most common in India
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Match the following local storms with their correct definition:
I. Mango Shower - A) Pre-Monsoon showers which help in blossoming of coffee flowers
II. Blossom Shower - B) Pre-Monsoon showers which help in the ripening of mangoes
III. Nor Westers - C) Hot, dry and oppressing winds blowing in Northern plains
IV. Loo - D) Evening thunderstorms in Bengal and Assam
Given below are some human activities:
A. Digging of mines
B. Constructing dams
C. Collection of leaves and herbs to sell them in the market
D. Weaving baskets from bamboo
E. Making leaf plates out of fallen leaves.
Which of the following statements are responsible for the disappearance of forests ?
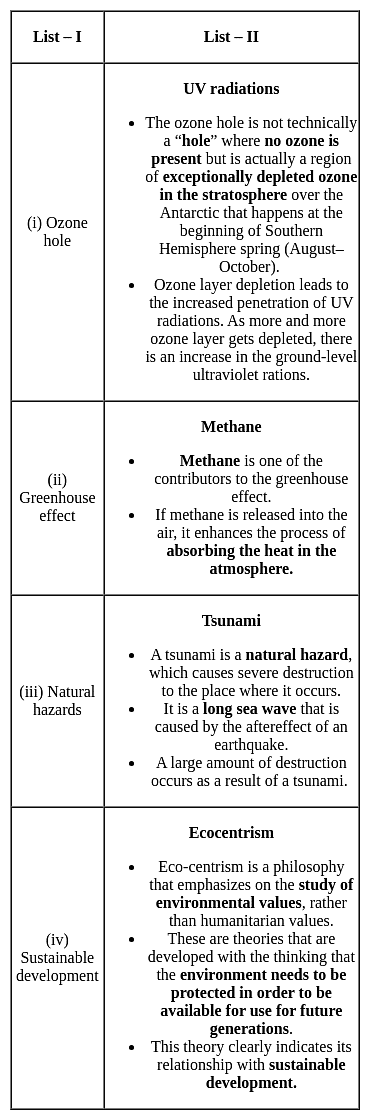
Match the concepts (List - I) with their proponents (List - II) selecting correct answer from the codes given below :
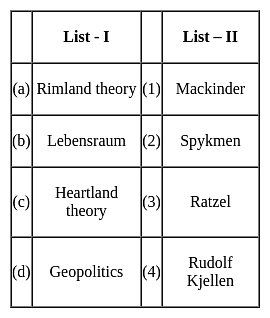
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below :
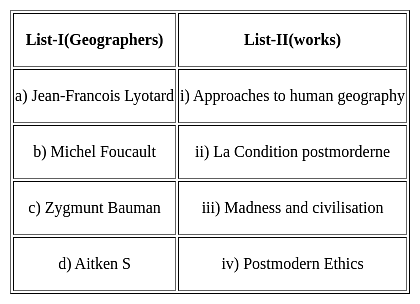
Choose the correct option from below:
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below :
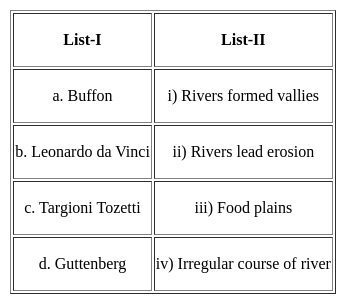
Choose the correct option from below:
Which of the following pairs of "Ocean- Maximum Deepest Point" is correct?
1. Pacific Ocean - Mariana Trench
2. Indian Ocean - Sunda Trench
Choose the correct statement from below:
Statement I:The concentration of the economy in the core city begins as a result of innovation. capital accumulation and industrial growth.
Statement II: The pre-industrial (agricultural) society, with localized economies and a small-scale settlement structure.
Consider statements (A) and (B) and choose the correct option.
(A) The coastline of Indian ocean is identical and irregular.
(B) The indented and irregular coastline provides ideal location for natural harbours and ports.
Which of the following is/are the ideal conditions for temperature inversion to occur?
A. Cloudy skies
B. Calm and stable air
C. Long summer days
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Mark the correct order of pressure belts from the equator to the poles:
A. Equatorial Low Belt
B. Subtropical High Belt
C. Sub-polar Low Belt
D. Polar High Belt
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the following pairs :
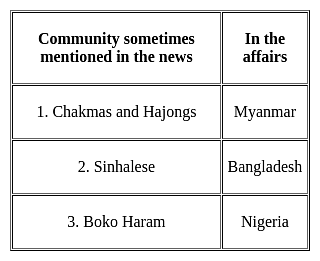
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
The earliest arrivals in India are believed to be Negritos. At which one of the following places are they mainly found now?
Which one of the following industries would be found in the traditional industrial region?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
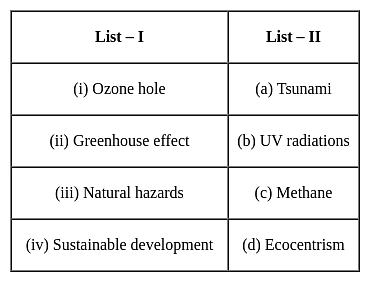
Which of the following is world's second largest producer of palm oil after Indonesia?
|
60 tests
|