APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 2 (Geography) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test APSET Mock Test Series 2025 - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 2 (Geography)
Which of the following is a minor plate of the lithosphere?
Consider the following statements regarding the distribution of pressure belts in the globe:
1. The sub-polar low belts are thermally induced and the temperature contrast between the subtropical and the polar regions gives rise to cyclonic storms here.
2. Only vertical currents are experienced in the equatorial low belt.
3. Calm conditions with feeble and variable winds are found in the subtropical high belt.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statement is correct about Fusion in remote sensing image interpretation?
What is remote sensing image interpretation? Choose the correct option.
Match the List - I with List - II and select the correct answer from the code given below :

i. In the last century, the world economy has experienced positive economic growth.
ii. There is a visible direct relationship between the GDP and the trade growth.
a. Flow maps tell us what is flowing or being migrated
b. It tells us about the direction of the movement
c. Flow maps give a general information about what is flowing and how it is flowing
d. Flow maps also tell us about the speed at which the flow occurs.
Which of the above statements are correct?
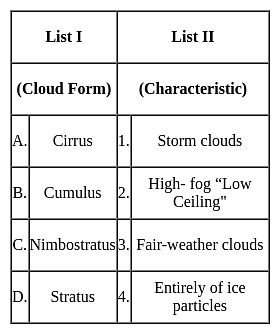
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists :
Which of the following statements about minerals are correct?
(A) Minerals are created by natural processes without any human interference
(B) Mica and chromite are nonferrous minerals
(C) Minerals lying at shallow depths are taken out through open cast mining
(D) Minerals are a non-renewable resource
Consider the following facts about the population of Scheduled Tribes:
1. The total population of Scheduled Tribes accounts for about 8% of the total population of the country.
2. Majority of the Scheduled tribe population live in rural areas and their population is around 10% of the total rural population of the country.
3. The share of the Scheduled Tribe population in urban areas is a meager 5%.
Which of the above is/are correct?Identify the rightly matched pairs:
1. Selvas - Amazon tropical rainforest
2. Prairies - Grasslands of Argentina and Uruguay
3. Pampas - Grasslands of North America
Select the correct answer from the options given below.(a) The khaddar soils are found in the low areas of valley bottom of the North Indian plains.
(b) The black regur soils are found in the Deccan plateau.
(c) The tarai region is area in the Deccan plateau.
(d) The foothills of Sahyadris have bhabar soils.
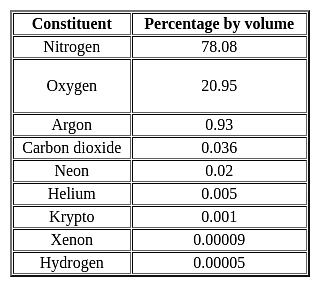
Major constituent gasses of the atmosphere are _____________.
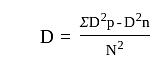
Solifluction is a geomorphic process involving a special type of soil flow that is noticed in
a. A special purpose map
b. Communicates geographical relationships
c. Shows single or multiple themes of a study
d. Depicts surface features of an area.
Which of the statements above are correct?
A geographer is analyzing global trade routes in the era of sailing ships. Which of the following two essential elements of geography would likely form the conceptual bases of the geographer's study?
Select the correct option(s) for the statement from the codes given below:
A region is more diverse culturally if it:
(a) has homogeneous population composition
(b) has heterogeneous population composition.
(c) receives voluminous in migration.
(d) is geographically isolated.
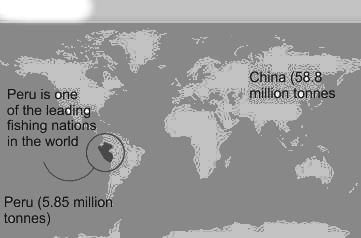
Which of the following is not among the four coral reef regions of India identified by the Government for intensive conservation and management?
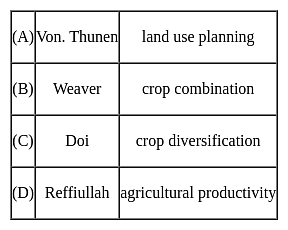
The following pairs are given about the contribution of geographer's in Agricultural geography and find out which is not correct?
According to the data, released by housing and urban poverity alleviation ministry, which state has the maximum number of slums?
|
60 tests
|