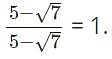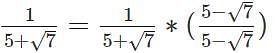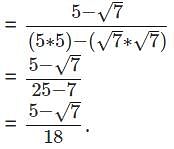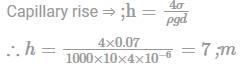HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test - 9 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test Series 2024 - HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test - 9
The sum of the digits of a number is subtracted from the number, the resulting number is always divisible by:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The average weight of a group of 15 persons increases by 2 kg when a person weighing 40 kg is replaced by Saurabh. What is the weight of Saurabh?
What is the area of a right-angled triangle with 12 meter base and 13 meter hypotenuse?
What is the average of all even numbers between 1 and 50?
The average of 100 numbers is 210. The average of these 100 numbers and 20 other new numbers is 200. What is the average of 20 new numbers?
A man walking at the rate of 9 km/hr crosses a tunnel in 5 minutes. What is the length of the tunnel?
The difference between a number and 12.50% of the same number is 252. What is 44.44% of the number?
By rationalising the denominator of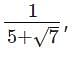 we get __________
we get __________
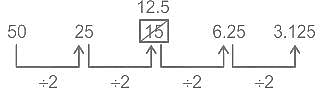
Find the wrong term in the given series?
50, 25, 15, 6.25, 3.125
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question.
Find the code for "dove"?
Statement I: 'steady matter ring' is coded as 'tv sf yz' and 'tease right dove' is coded as 'gl oz hv'.
Statement II: 'ring right figure' is coded as 'sf ev oz' and 'steady tease check' is coded as 'gl yz mf'.
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
K/T : 11/20 :: J/R : ?
Match List-I (SI Engine Operating Mode) with List –II (Appromimate A/F Ratio) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists
List - I (SI Engine Operational Mode)
A. Idling
B. Cruising
C. Maximum Power
D. Cold starting
List-II (A/F Ratio Supplied by the Carburetor)
1. 3
2. 10
3. 13
4. 16
5. 20
Which one of the following is defined as force per unit length?
Bending moment M and torque T are applied on a solid circular shaft. If the maximum bending stress equals maximum shear stress developed, then M is equal to
Consider the following joints:
1. Railway carriage wheel and axle
2. IC engine cylinder and liner
which of the above joints is /are the result (s) of interference fit ?
The principal source of pollutant Hydrogen Sulphide in the air is
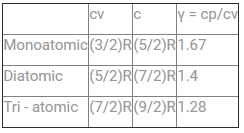
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?
Hardness of cementite is of the order of _______ BHN
Which of the following statements is wrong?
If a capillary of diameter 4 × 10-6 m is used, determine the capillary rise in water (σw = 0.07N/m, g = 10 m/s2).
A transducer that converts a physical input quantity into electrical output in the form of a pulse is known as
A circular bar 20 mm in diameter and 200 mm long is subjected to a force of 20 kN. Find the strain in the bar if the value of E = 80 GPa.
Kinematic pairs are those which have two elements that



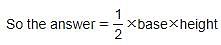
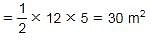
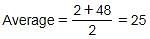
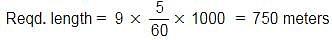
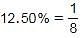
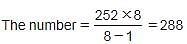
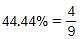
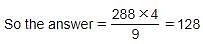
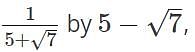 we will get same expression since
we will get same expression since