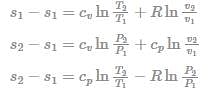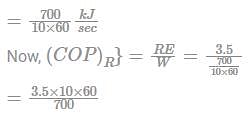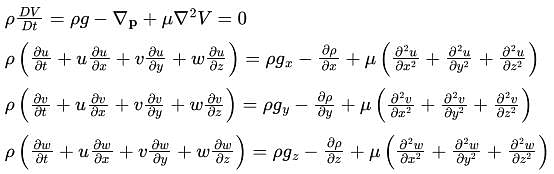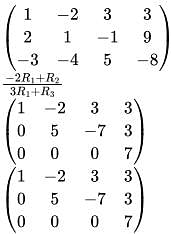UPSSSC JE Mechanical Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPSSSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2024 - UPSSSC JE Mechanical Paper 2 Mock Test - 5
The first law of thermodynamics deals with ___.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The thickness of oil film between gauge block is of the order of
The molecular mass expressed in gram (i.e. 1 gmole) of all gases, at N. T. P., occupies a volume of
In which of the following operations performed on the lathe machine, chips do not occur?
One kg of air (R=287 J/kg-K) goes through an irreversible process between two equilibrium states, 1 (30°C, 1.2 m3) and state 2 (30°C, 0.8 m3). What is the change in entropy (in J/kg-K)?
The ratio of the depth of the bucket for a Pelton wheel to the diameter of a jet is of the order of _____.
For the given two statements:
I. The performance of an SI engine can be improved by increasing the compression ratio.
II. Fuels of higher-octane numbers can be employed at a higher compression ratio.
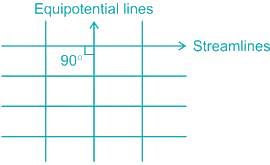
What is the value of the angle (degree) between streamlines and equipotential lines at the point of intersection in the flow net?
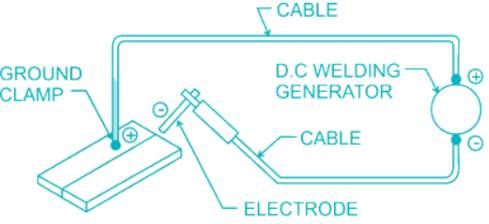
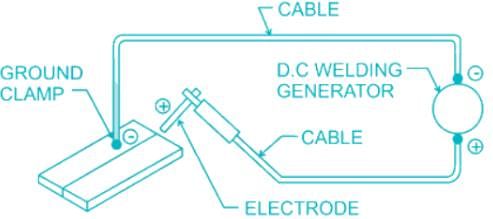
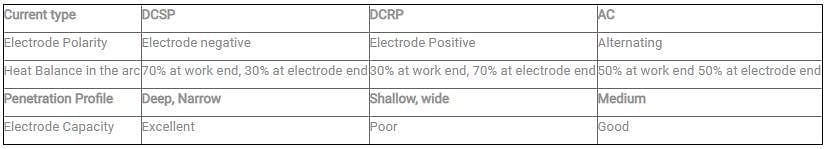
In arc welding, penetration is minimum for
Which of the following statements is wrong?
At the triple point of a pure substance, the number of degrees of freedom is
Cutting and forming operations can be performed in a single operation in a _______ die.
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?
Work done obtained in a free expansion process is_______.
A substance is said to be volatile if it has______
The velocity of a freely falling object is
Which of the following is a medium head turbine in which water flows inwards radially?
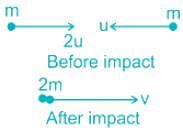
Two particles, each of mass m, collide head-on when their speeds are 2u and u. If they stick together on impact, find their combined speed in terms of u.
In the case of power transmission through pipes, maximum efficiency is
Which of the following statements is not true for diamond?
The two reference fuels used for cetane rating are
Atmospheric pressure at ground level is approximately:
A man is climbing up a ladder up a ladder which is resting against a vertical wall. When he wasexactly half way up, the ladder started slipping . The path traced by the man is :
The motion of the particle is described by the following equations. x = t2 + 8t + 4 find the velocity when t = 2 sec
The following system of equations :
x - 2y + 3z = 3
2x + y - z = 9
-3x - 4y + 5z = - 8 has