HPCL Electrical Engineer Mock Test - 1 - PSSSB Clerk MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Electrical Engineer Mock Test - 1
Two persons start running towards each other, one from A to B and the other from B to A. They cross each other in one hour. The first person reaches B 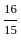 hours before the second person reaches A. If the distance between A and B is 8 km, then find the speed of the faster man.
hours before the second person reaches A. If the distance between A and B is 8 km, then find the speed of the faster man.
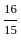 hours before the second person reaches A. If the distance between A and B is 8 km, then find the speed of the faster man.
hours before the second person reaches A. If the distance between A and B is 8 km, then find the speed of the faster man.In a single throwing of a dice, the probability of getting more than 4 is 1/3 then probability of getting 4 or less than 4 will be
The distance between stations A and B is 778 kilometres. A train travels from station A to station B at a uniform speed of 84 km/h and then returns to station A at a uniform speed of 56 km/h. What is the train's average speed (in km/h) throughout the journey?
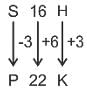
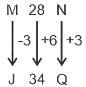
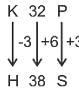
S16H is related to P22K in a certain way. In the same way, M28N is related to J34Q. To which of the following is K32P related following the same logic?
Select the option that can be used as a one-word substitute for the given group of words.
Someone in love with himself
Rs. 6000 is lent at the rate of 8 percent per annum on compound interest (compounded quarterly). What will be the compound interest of 6 months?
The following line graph represents the sale of the number of Burgers at a shop for the seven days.
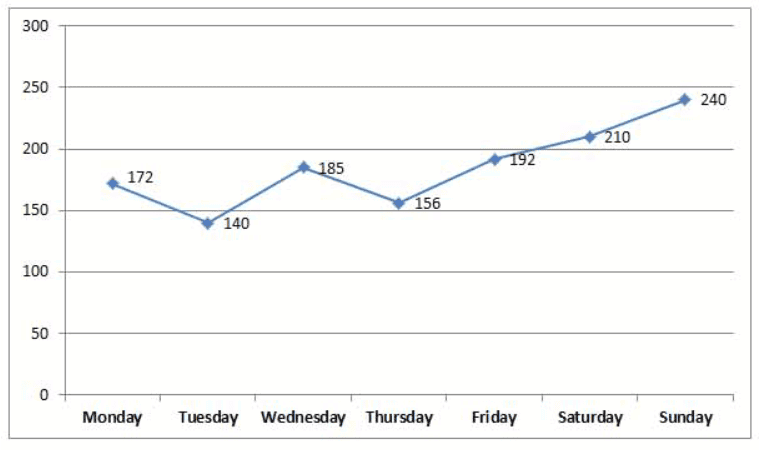
On which day, the number of burgers sold is equal to the average number of burgers sold by the shopkeeper during the given period?
In a certain code language, “dom pull ta” means - “bring hot food”, “pull tir sop” means “food is good” and “tak da sop” means “good bright boy”. Which of the following means “hot” in the same code language?
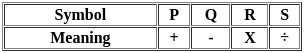
If P denotes '+', Q denotes '-', R denotes '×' and S denotes '÷', then which of the following is correct?
Match the following:
Instrument type
P) Permanent magnet moving coil
Q) Moving iron connected through current transformer
R) Rectifier
S) Electrodynamometer
Used for
1. DC only
2. AC only
3. DC and AC
The scalar product of two non zero vectors will be zero, if and only if the angle between two vectors is:
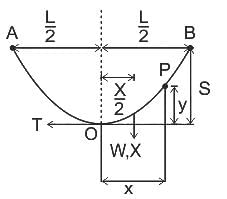
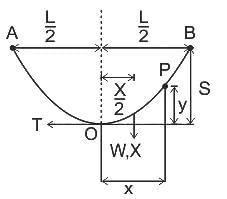
In the figure shown above, if AOB is the conductor, A and B are points of supports. Then which of the following is expression to calculate sag? (assume all other quantities with usual notations)
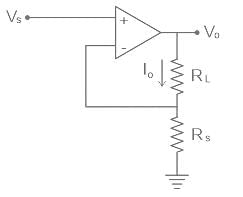
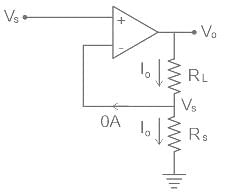
An Op-amp based circuit is shown in figure below. Current I0 is
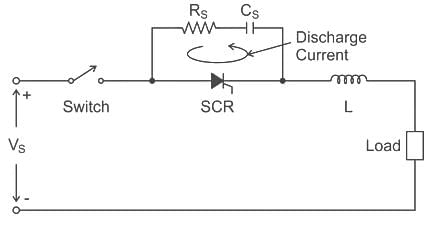
False turn-on of SCR by large dv/dt can be prevented by using a _______ with the SCR.
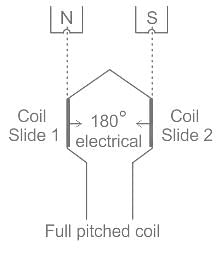
A 4-pole, 3-phase star connected alternator has 48 slots. The coil span is 120 electrical degrees. Determine the coil span factor.
Gas-insulated substation is smaller than conventional substation because of:
1. high insulation property of SF6 gas
2. high dielectric property of SF6 gas
3. high electronegative property of SF6 gas
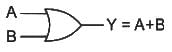
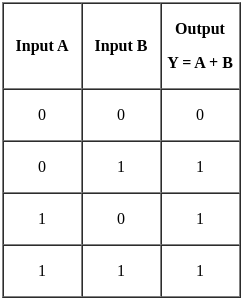
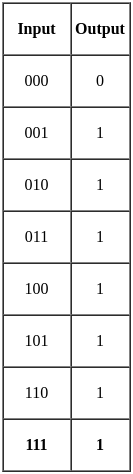
A two-input logic gate is giving low output when both the inputs are low. For all other input conditions, the output is high. Select the correct logic gate.
The magnetic flux Φ(in Web) linked with a single turn coil at an instant of time t (in second) is given by Φ(t) = 2t2 – 20t + 40. The induced EMF in the coil at the instant t = 2 seconds is
Match the following:
Instrument type
P) Permanent magnet moving coil
Q) Moving iron connected through current transformer
R) Rectifier
S) Electrodynamometer
Used for
1. DC only
2. AC only
3. DC and AC


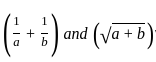 is –
is –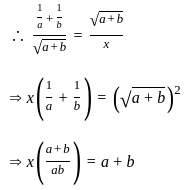


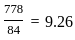 hours
hours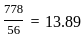 hours
hours km/h
km/h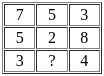
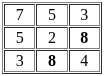
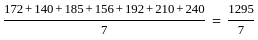 = 185
= 185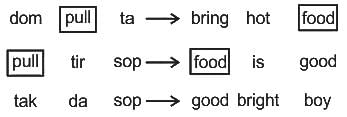

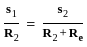
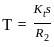
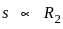
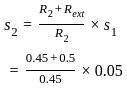
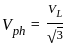
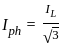
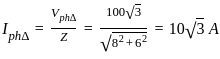
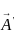 and
and 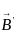 are two vectors and
are two vectors and 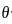 is angle between them,
is angle between them,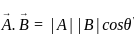
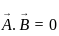
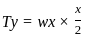
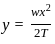 ---1
---1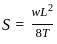
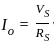
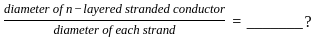
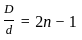
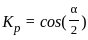
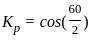


 ⇒ flux linkages (Wb – turns)
⇒ flux linkages (Wb – turns)
 = Rate of changes in flux (Wb/sec)
= Rate of changes in flux (Wb/sec)













