Test: Gametogenesis (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Gametogenesis (NCERT)
2n=16 is in a primary spermatocyte which is in metaphase of first meiotic division. What shall be the total number of chromatids in each of the secondary spermatocyte?
The second maturation division of the mammalian ovum occurs
In humans, at the end end of the first meoitic division, the male germ cells differentiate into the
Consider the following statements each with two blanks.
(A) Seminiferous tubules produce (i) while Leydig's cells produce (ii).
(B) In females, urethra is small and conducts (iii) while in males it conducts urine and (iv).
(C) The process of formation of spermatozoa from spermatogonia is called (v) and the process of maturation of spermatids into spermatozoa is called (vi).
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (i) to (vi) in the statements?
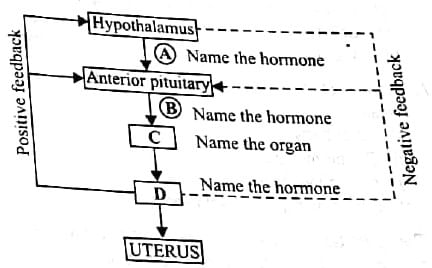
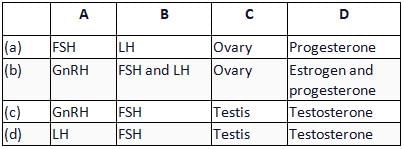
Given below is an incomplete flow chart showing influence of hormones on gametogenesis in human females. Study it carefully and identify A, B, C and D.
Rakesh and Reshma have difficulty conceiving a baby. They consulted a sex therapist. Sperm count of Rakesh was normal but the doctor observed that the motility of his sperm was less. What part of sperm do you think has the issue?
The sperms undergo physiological maturation, acquiring increased motility and fertilizing capacity in
At what stage of life is oogenesis initiated in a humanfemale?
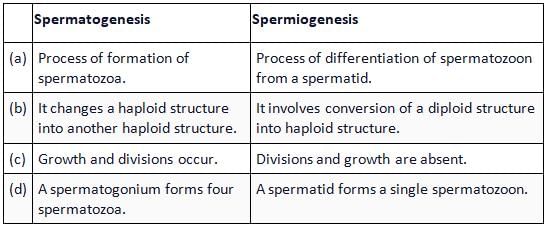
The given table shows differences between spermato genesis and spermiogenesis. Select the incorrect option.
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a mature human testis is
During oogenesis, each diploid , primary oocyte produces
Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as
Which of the following is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male?
How many sperms are formed from 4 primary spermatocytes?
Which of the following contains the actual genetic part of a sperm?
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|