Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Inheritance & Variation - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Inheritance & Variation
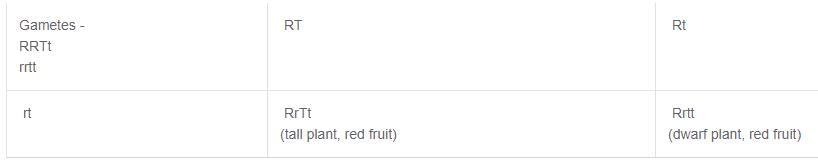
In a plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with RRTt genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt:
What will be expected blood groups in the off spring when there is a cross between AB blood group mother and heterozygous B blood group father?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following amino acid substitutions in the beta chain of the haemoglobin molecule leads to the development of sickle cell anaemia?
Two genes p and q showing 1.3% of recombination while other two genes x and y show 37.2 percent of recombination. Which pair of genes is close to each other?
Assertion: An organism with lethal mutation may not even develop beyond the zygote stage.
Reason: All types of gene mutations are lethal.
Column I
i. Down’s syndrome
ii. Klinefelter’s syndrome
iii. Turner’s syndrome
Column II
a. Broad palm with characteristic palm crease
b. Gynaecomastia
c. Rudimentary ovaries
d. XO
e. XXY
f. Physical development is retarded.
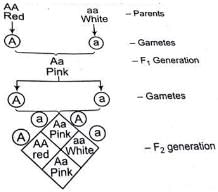
F2 generation in a Mendelian cross showed that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are same as 1 : 2 : 1. It represents in case of
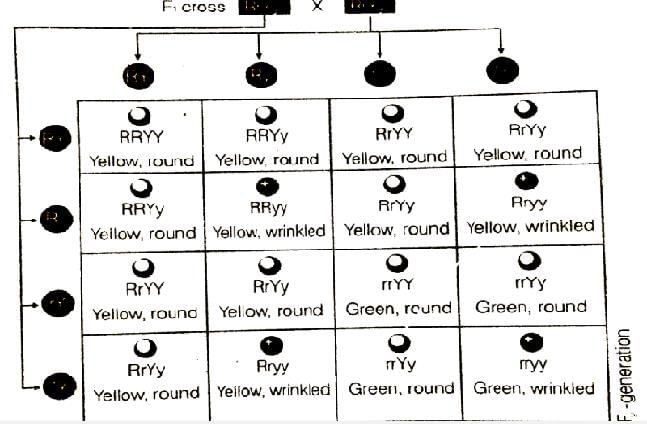
In Mendel's experiments with garden pea, round seed shape (RR) was dominant over Wrinkled Seeds (rr), Yellow cotyledon (YY) was dominant over green cotyledon (yy). What are the expected Phenotypes in the F2 generation of the cross RRYY x rryy?
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?
Crossing over occurs at:
Deviation from Medelism’s occurs due to
a. Multiple alleles
b. Co dominance
c. Linkage and crossing over
d. Independent assortment
Find the correct match:
Chromosome theory of XY sex determination was proposed by:
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?
(i) Polyploidy is caused due to failure of cytokinesis after telophase.
(ii) Polyploidy results in an increase in the number of autosomes.
(iii) Turner’s syndrome is an example of polyploidy.
(iv) Polyploidy results in an increase in a whole set of chromosomes.
Which of the following would not be a feature seen in a patient with the following karyotype?
Assertion: In human beings, 23 pairs of chromosomes are present in diploid cells.
Reason: 22 pairs of chromosomes are equal in male and female but a pair sex chromosome is different in them.
Linkage is the_________.
Column I
a. Phenylketonuria
b. Down's syndrome
c. Klinefelter's syndrome
d. Turner's syndrome
Column II
i. Autosomal trisomy associated with mongolism
ii. Gynaecomastia
iii. Autosomal recessive trait associated with mental retardation
iv. Sterile females with rudimentary ovaries
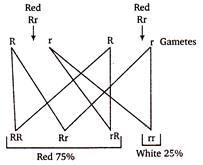
If two pea plants having red (dominant) coloured flowers with unknown genotypes are crossed, 75% of the flowers are red and 25% are white. The genotypic constitution of the parents having red coloured flowers will be
Which of the following statements is true regarding the “law of independent assortment”?
On the basis of sex chromosome shown below, the bird shown is:
In a given plant, red colour (R) of fruits is dominant over white fruit (r): and tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfness (t). If a plant with genotype RRTt is crossed with a plant of genotype rrtt, what will be the percentage of tall plants with red fruits in the next generation?
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|