Test: Asexual Reproduction (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Asexual Reproduction (Old NCERT)
During binary fission in Amoeba which of the following organelles is duplicated?
In which of the following plants, vegetative propagation occurs by adventitious buds?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Refer the given figures and select the correct option.
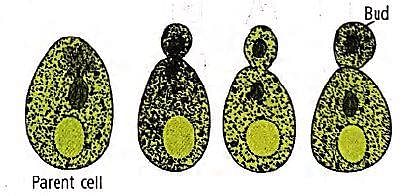

Read the following statements about asexual reproduction and select the correct ones.
(i) It involves a single parent.
(ii) It is slower than sexual reproduction.
(iii) It produces progeny that are genetically identical with the parent but not with one another.
(iv) The progeny of asexual reproduction can be termed as clones.
March Column-l with Column-ll and select the correct options from the codes given below.
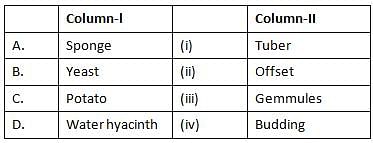
Codes:
a. A-(iv), B- (i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
b. A-(iii), B- (i), C-(iv), D-(ii)
c. A-(iii), B- (iv), C-(i), D-(ii)
d. A-(iv), B- (ii), C-(i), D-(iii)
Refer the given figures and select the correct option.
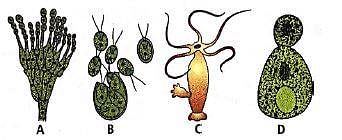
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Conidia are the asexual propagules restricted to kingdom fungi.
(ii) A piece of potato tuber having at least one eye (or node) is capable of giving rise to a new plant.
(iii) Ginger propagates vegetatively with the help of its underground roots.
(iv) Fleshy buds which take part in vegetative propagation are called bulbils, present in Dioscorea, Agave, etc.
____________ is a life process that is not essential for an individual's survival but for survival of the species.
Read the following statements about 'Terror of Bengal' and select the correct ones.
(i) Terror of Bengal' is the name given to water hyacinth (Eichhornia), an algae.
(ii) Eichhornia was introduced in India due to its aesthetic value.
(iii) Eichhornia drains oxygen from the water which leads to death of fishes.
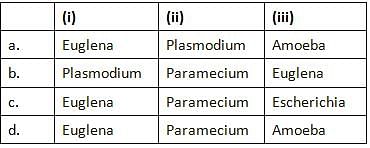
Refer the given figures which show three different types of fission. Select the option which correctly matches them with the organism in which they occur.
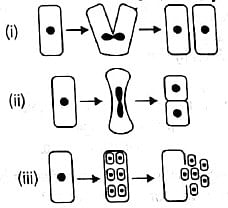
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Many plants are propagated vegetatively even though they bear seeds.
Statement 2: Sweet potatoes multiply vegetatively by root tubers.
It is a common method of vegetative propagation in which 20 - 30 cm long pieces of one year old stems are cut, their lower ends are dipped in root promoting hormones and are then planted in the soil, which then develop adventitious roots. This method of vegetative propagation is performed in
Vegetative propagation is the term used for
'Clones' are individuals that have exactly the same
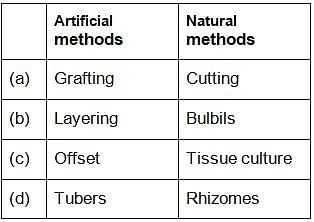
Which of the following options correctly identities artificial and natural methods of vegetative propagation?
Which of the following cannot serve as a vegetative propagule?
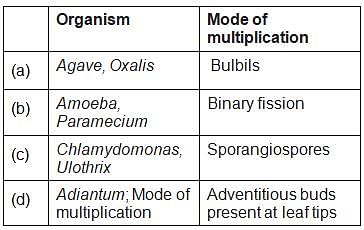
Select the mismatched pair of organism and their mode multiplication.
Which of the following is not used for vegetative propagation?
Which of the following options shows two plants in which new plantlets arise from the same organ?
Which one of the following processes results in the formation of a clone of bacteria?
|
87 videos|294 docs|185 tests
|

















