Test: Nuclei - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Nuclei
What percentage of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus?
In the mass number range A = 30 to 170, the binding energy per nucleon is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Plutonium decays with a half-life of 24000 years. If the plutonium is stored for 72000 years, then the fraction of plutonium that remains is
B210has a half life of 5 days. The time taken for seven-eighth of a sample to decay is
If 10% of a substance decays in 10 days, then approximate percentage of substance left after 24 days is
Choose the WRONG statement. A thermonuclear fusion reactor is better than a fission reactor for the following reason:
A radioactive substance has a half life of four months. Three fourths of the substance will decay in
At a given time there are 25% undecayed nuclei in a sample. After 10 seconds number of undecayed nuclei reduces to 12.5%. Then mean life of the nuclei will be about
Which of the following particles can be added to the nucleus of an atom without changing its chemical properties?
Relation between atomic number (Z), neutron number (N) and mass number (A) is
The half life of radon is 3.8 days. After how many days will only one twentieth of a radon sample be left over?
90% of a radioactive sample is left undisintegrated after time τ has elapsed, what percentage of initial sample will decay in a total time 2τ?
The average number of neutrons released by the fission of one uranium atom is
The nuclei of isotopes of a given element contain the same number of
A radioactive material decays by simultaneous emission of two particles with respective half lives 1620 and 810 years. The time in years, after which one fourth of the material remains is
|
98 videos|387 docs|104 tests
|


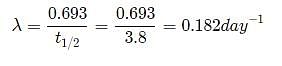 Let the initial amount of radon be N0 and the amount left after t days be N which is equal to N0/2
Let the initial amount of radon be N0 and the amount left after t days be N which is equal to N0/2