Test: Thermodynamics Level - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Test: Thermodynamics Level - 1
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following variables controls the physical properties of a perfect gas
Which of the following laws is applicable for the behaviour of a perfect gas
According to kinetic theory of gases, the absolute zero temperature is attained when
According to Gay-Lussac law for a perfect gas, the absolute pressure of given mass varies directly as
According to Dalton's law the total pressure of the mixture of gases is equal to
The value of n = 1 in the polytropic process indicates it to be
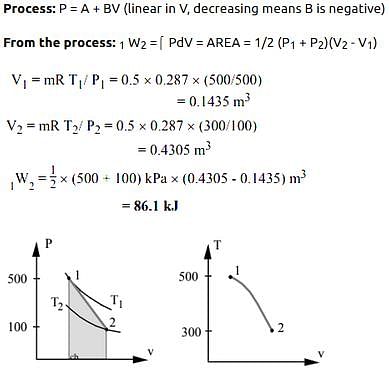
A piston cylinder contains 0.5 kg of air at 500 kPa and 500 K. The air expands in a process so pressure is linearly decreasing with volume to a final state of 100 kPa and 300 K. Find the work in the process.
The pressure of a gas in terms of its mean kinetic energy per unit volume E is equal to
Kinetic energy of the molecules in terms of absolute temperature (T) is proportional to
One kg of carbon monoxide requires __________ kg of oxygen to produce 11/7 kg of carbon dioxide gas.
The condition of perfect vacuum, i.e., absolute zero pressure can be attained at
Specific heat of air at constant pressure is equal to
To convert volumetric analysis to gravimetric analysis, the relative volume of each constituent of the flue gases is
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|