Test: Chemical Equilibrium - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Chemical Equilibrium - 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Does Le-Chatelier’s principle predict a change of equilibrium concentrations for the following reaction if the gas mixture is compressed:
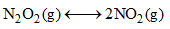
The plot given below shows the relation between (1/T) and log(s), where S is the solubility of an electrolyte AB and T is the temperature in Kelvin. What conclusion can be drawn from the plot:
A mixture of 2 mole each of helium and an unknown gas (normal boiling point = 0°C) is kept in a 22.4 L flask. If the flask is cooled to 0.1°C, the resultant pressure (in atm) inside the flask is:
For the complete oxidation of 100 g of Cyclohexanol to cyclohexanon, the quantity of CrO3 required is (assuming 100% chemical yield) [Atomic wt. of Cr = 52)
For the reaction: the equilibrium constant at 2000 K and 1.0 bar is 5.25. When the pressure is increased by 8-fold, the equilibrium constant:
In a chemical reaction,
The total pressure at equilibrium is 6 atm. The value of equilibrium constant is:
If the equilibrium constants for the reactions 1 and 2
Are K1 and K2, the equilibrium constant for the reaction
Consider the reaction, at equilibrium,
The equilibrium can be shifted towards the forward direction by:
When a reversible reaction is followed with time with initial concentration of A being 0.6 mol. L–1, the following graph is obtained:
The equilibrium constant K, for the above reaction is:
If the equilibrium reaction is heated, it is observed that the concentration of A increases. Then,
Consider the reaction:
The unit of the thermodynamic equilibrium constant for the reaction is:
For the reaction H2(g)+I2(g)⇌2HI (g) at 721 K
value of equilibrium constant is 50, when molar concentration of both hydrogen and iodine is 0.5 M at equilibrium value of Kp under the same conditions will be
A 2 L vessel containing 2g of H2 gas at 27°C is connected to a 2L vessel containing 176 g of CO2 gas at 27°C. Assuming ideal behaviour of H2 and CO2, the partial pressure of H2 at equilibrium is………bar.
The relationship between the equilibrium constant K1 for the reaction
And the equilibrium constant K2 for the reaction
The hydrolysis constant (Kh) of NH4Cl is 5.6×10–10. The concentration of H3O+ in a 0.1 M solution of NH4Cl at equilibrium is:
The equilibrium constant Kc for the following reaction at 842°C is 7.90 × 10–3. What is Kp at same temperature:
For the equilibrium what is the temperature at which
The pH of a solution of hydrochloric acid is 4. The molarity of the solution is:
Consider the following gaseous equilibria given below
The equilibrium constant for the reaction, in terms of K1, K2 and K3 will be
9.2 grams of N2O4(g) is taken in a closed on litre vessel and heated till the following equilibrium is reached
At equilibrium, 50% N2O4(g) is dissociated. What is the equilibrium constant (in mol litre–1) (molecular weight of N2O4 = 92)
In a chemical reaction: xenon gas is added at constant volume. The equilibrium:
The equilibrium constants for the reactions and
are K1 and K2, respectively. The equilibrium constant for the reaction
is
Correct statement on the effect of addition of aq. HCl on the equilibrium is:
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|

















