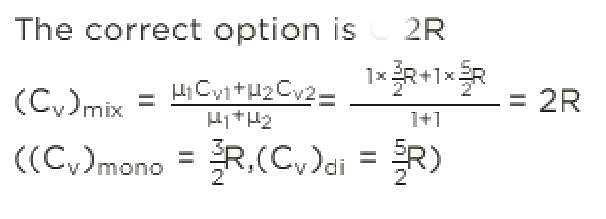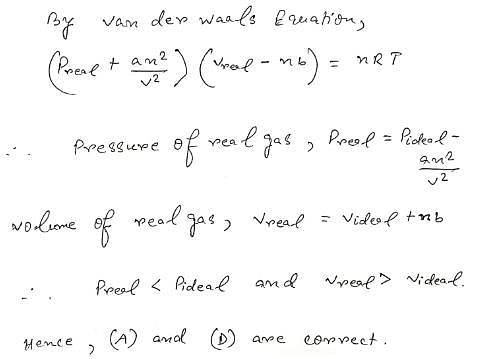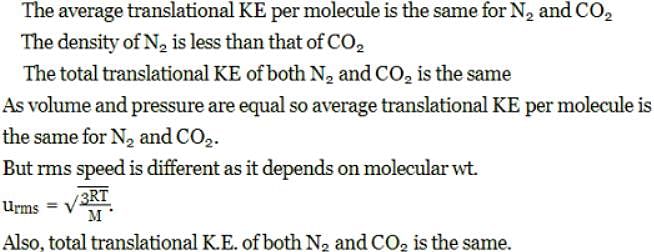Test: Gaseous State - 6 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Gaseous State - 6
A gas absorbs a photon of 355 nm and emits at two wavelengths. If one of the emissions is at 680 nm, the other is at:
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is mixed with 1 mole of an ideal diatomic gas. The molar specific heat of the mixture at constant volume is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
According to kinetic theory of gases, for a diatomic molecule:
The ratio between the rms velocity of H2 at 50 K and that of O2 at 800 K is:
X mL of H2 gas effuses through a hole in a container in 5 seconds. The time taken for the effusion of the same volume of the gas specified below under identical conditions is:
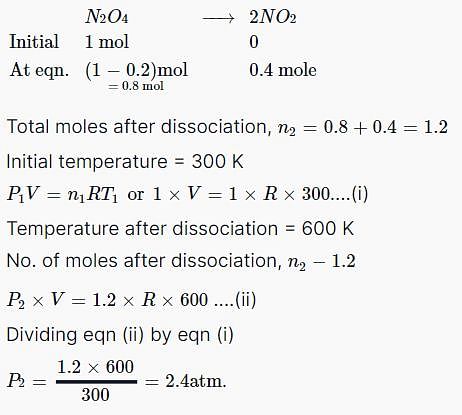
One mole of N2O4(g) at 300 K is kept in a closed container under one atmosphere. It is heated to 600 K when 20% by mass of N2O4(g) decomposes to NO2(g). The resultant pressure is:
When a gas is passed through a small hole at a temperature greater then its critical temperature, Joule-Thomson effect will show:
Which of the following choice(s) is (are) correct for a gas:
The average velocity of anideal gas molecule at 27°C is 0.3 m/s. The average velocity at 927°C will be:
Which of the fo llowing is/are correct?
(I) If liquid “kryptonite” (from Superman’s home planet), with a density twice that of mercury, is used in a barometer on earth, one standard atmosphere of pressure would support a column of mercury 380 mm in height.
(II) At constant volume and number of moles of gas, the pressure exhibited by an ideal gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
(III) At standard temperature and pressure (STP), the volume of a mixture of gases containing 0.400 mol H2, 0.600 mo l N2, and 1.00 mol of O2 is 44.8 L and the mole fraction of N2 is 0.300.
Which of the following is(are) true for the real gases. (‘C’ represents so me constant value, ‘R’ represents molar gas constant).
What conclusion would you draw from the following graphs for an ideal gas:
Indicate the correct statement for equal volume of N2(g) and CO2(g) at 25°C and 1 atm:
Which of the following is correct for critical temperature:
Consider the following statement regarding Maxwell’s distribution of velocities. The correct statement(s) is/are:
If a gas expands at a constant pressure by providing heat:
Following represents the Maxwell distribution curve for an ideal gas at two temperature T1 and T2. Which of the following option(s) are true?
Which graphs represent the deviation fro mideal gas for H2:
Consider the following statements. If the van der Waal’s parameters of two gases are given as
Then:
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|