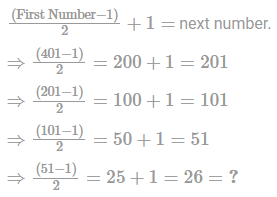Goa PCS Pre-Screening Mock Test- 6 - GPSC (Goa) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GPSC (Goa) Mock Test Series 2024 - Goa PCS Pre-Screening Mock Test- 6
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order all are seated at equal distance, all are facing in same direction. All of them have a lucky number i.e. 141, 242, 324, 384, 427, 835, 844, and 960 but not necessarily in the same order.
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Q. How many persons sit between E and the one, whose lucky number is 242?
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order all are seated at equal distance, all are facing in same direction. All of them have a lucky number i.e. 141, 242, 324, 384, 427, 835, 844, and 960 but not necessarily in the same order.
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Q. Who among the followings sits immediate left of the one who is 3rd to the left of H?
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order all are seated at equal distance, all are facing in same direction. All of them have a lucky number i.e. 141, 242, 324, 384, 427, 835, 844, and 960 but not necessarily in the same order.
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Q. What is the lucky number of E?
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order all are seated at equal distance, all are facing in same direction. All of them have a lucky number i.e. 141, 242, 324, 384, 427, 835, 844, and 960 but not necessarily in the same order.
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Q. Who sits immediate left of C?
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order all are seated at equal distance, all are facing in same direction. All of them have a lucky number i.e. 141, 242, 324, 384, 427, 835, 844, and 960 but not necessarily in the same order.
E’s lucky number is 2.5 times of D’s lucky number. D is not an immediate neighbor of C and the one whose lucky number is 835. There is an angle of 1800 degree between H and G who is not an immediate neighbor of D. The one whose lucky number is 844 and the one whose lucky number is an odd number as well as not divisible by 7 sit opposite to each other. There is an angle of 135 ̊ between F and the one whose lucky number is 141. C sits at 900 degree clockwise direction of A. F’s lucky number is 7th highest and is not an immediate neighbor of C. Lucky number of the one, who sits 2nd to right of C is an odd palindrome number. G’s lucky number is perfect square. There is an angle of 90 ̊ between A and B. C’s lucky number is 7th lowest number.
Q. What is the lucky number of the one who sits 2nd right of F?
Directions: In the given questions, assuming the given statements to be true. Find which of the given four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV is/are definitely true and give your answer accordingly.
Q. Statement: S > M ≥ D > H ≤ R ≤ T < W
Conclusions:
I. S > H
II. W > H
III. R < W
IV. M > T
Directions: In the given questions, assuming the given statements to be true. Find which of the given four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV is/are definitely true and give your answer accordingly.
Q. Statement: M > U > L ≤ N; L ≥ Y > A
Conclusions:
I. Y < N
II. M>N
III. N = Y
IV. M > A
Directions: In the given questions, assuming the given statements to be true. Find which of the given four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV is/are definitely true and give your answer accordingly.
Q. Statement: J ≥ A > D = E; L < A < M
Conclusions:
I. M < J
II. J > L
III. D > L
IV. E < M
Directions: In the given questions, assuming the given statements to be true. Find which of the given four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV is/are definitely true and give your answer accordingly.
Q. Statement: Y > F ≤ O ≤ P; F ≥ U < T
Conclusions:
I. Y > P
II. T < F
III. O > T
IV. P < U
Directions: In the given questions, assuming the given statements to be true. Find which of the given four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV is/are definitely true and give your answer accordingly.
Q. Statement: K ≤ O < M D = T;
Conclusions:
I. T < E
II. K > J
III. T > O
IV. E < M
Directions : Study the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Six persons A, B, C, D, E and F are comparing their weights and each of them is having a different weight. D is heavier than only two persons. E is the only person heavier than F and lighter than D. C’s weight is less than only B’s weight. The third heaviest weight is 150kgs and the fifth heaviest weight is 110kgs.
Q. What is the possible weight of D?
Directions : Study the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Six persons A, B, C, D, E and F are comparing their weights and each of them is having a different weight. D is heavier than only two persons. E is the only person heavier than F and lighter than D. C’s weight is less than only B’s weight. The third heaviest weight is 150kgs and the fifth heaviest weight is 110kgs.
Q. If the heaviest weight is 50kgs more than A’s weight, then what is the possible weight of C?
If 2 is subtracted from each odd digit in the number 7854392 and 1 is added to each even digit in number then which of the following digit is repeated in the digits so obtained?
How many such pairs of letters are there in the word “MANGO” each of which has as many letters between them in the word as in the English alphabet?
In a certain code, MAIN is written as IMNA and GOAL is written as AGLO. How is DUSK written in that code?
Directions : Study the information and answer the following questions.
In a certain code
‘always to be right’ is written as ‘4 9 3 2’
‘right is also just’ is written as ‘9 7 6 5’
‘come to terms is written as ‘1 3 8’,
terms are just’ is written as ‘0 1 6’ and
‘always is’ is written as ‘7 4’.
Q. What does ‘6’ represent in this code?
Directions : Study the information and answer the following questions.
In a certain code
‘always to be right’ is written as ‘4 9 3 2’
‘right is also just’ is written as ‘9 7 6 5’
‘come to terms is written as ‘1 3 8’,
terms are just’ is written as ‘0 1 6’ and
‘always is’ is written as ‘7 4’.
Q. Which of the following is the code for ‘right’?
Directions : Study the information and answer the following questions.
In a certain code
‘always to be right’ is written as ‘4 9 3 2’
‘right is also just’ is written as ‘9 7 6 5’
‘come to terms is written as ‘1 3 8’,
terms are just’ is written as ‘0 1 6’ and
‘always is’ is written as ‘7 4’.
Q. Which of the following represents ‘always be right terms’?
Directions : Study the information and answer the following questions.
In a certain code
‘always to be right’ is written as ‘4 9 3 2’
‘right is also just’ is written as ‘9 7 6 5’
‘come to terms is written as ‘1 3 8’,
terms are just’ is written as ‘0 1 6’ and
‘always is’ is written as ‘7 4’.
Q. Which of the following can be coded as ‘86315’ ?
Directions : Study the information and answer the following questions.
In a certain code
‘always to be right’ is written as ‘4 9 3 2’
‘right is also just’ is written as ‘9 7 6 5’
‘come to terms is written as ‘1 3 8’,
terms are just’ is written as ‘0 1 6’ and
‘always is’ is written as ‘7 4’.
Q. Which of the following is the code for ‘come’?
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions :
Ten persons are sitting in two parallel rows containing five persons each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row —1, J, K, L, M, and N are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all or them are facing south. In row-2, V, W, X, Y and Z are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing north. Therefore in the given seating arrangement each member seated in row faces another member of the other row. Z sits third to the right of W. V sits second to the left of Z. The person facing V sits to the immediate right of K. Only one person sits between K and M. J is not an immediate neighbour of K. Only two persons sit between J and L. Neither K nor J faces Y.
Q. Who amongst the following is facing N?
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions :
Ten persons are sitting in two parallel rows containing five persons each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row —1, J, K, L, M, and N are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all or them are facing south. In row-2, V, W, X, Y and Z are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing north. Therefore in the given seating arrangement each member seated in row faces another member of the other row. Z sits third to the right of W. V sits second to the left of Z. The person facing V sits to the immediate right of K. Only one person sits between K and M. J is not an immediate neighbour of K. Only two persons sit between J and L. Neither K nor J faces Y.
Q. Which of the following statements is true regarding M?
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions :
Ten persons are sitting in two parallel rows containing five persons each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row —1, J, K, L, M, and N are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all or them are facing south. In row-2, V, W, X, Y and Z are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing north. Therefore in the given seating arrangement each member seated in row faces another member of the other row. Z sits third to the right of W. V sits second to the left of Z. The person facing V sits to the immediate right of K. Only one person sits between K and M. J is not an immediate neighbour of K. Only two persons sit between J and L. Neither K nor J faces Y.
Q. Who amongst the following is facing X?
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions :
Ten persons are sitting in two parallel rows containing five persons each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row —1, J, K, L, M, and N are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all or them are facing south. In row-2, V, W, X, Y and Z are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing north. Therefore in the given seating arrangement each member seated in row faces another member of the other row. Z sits third to the right of W. V sits second to the left of Z. The person facing V sits to the immediate right of K. Only one person sits between K and M. J is not an immediate neighbour of K. Only two persons sit between J and L. Neither K nor J faces Y.
Q. What is the position of Z with respect of Y?
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions :
Ten persons are sitting in two parallel rows containing five persons each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row —1, J, K, L, M, and N are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all or them are facing south. In row-2, V, W, X, Y and Z are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing north. Therefore in the given seating arrangement each member seated in row faces another member of the other row. Z sits third to the right of W. V sits second to the left of Z. The person facing V sits to the immediate right of K. Only one person sits between K and M. J is not an immediate neighbour of K. Only two persons sit between J and L. Neither K nor J faces Y.
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on the given arrangement and hence form a group. Which of them does not belong to that group?
In each of these questions two equations numbered (i) and (ii) are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer, if –
(i) p² - 24p + 144 = 0
(ii) q ² - 26q + 169 = 0
If 12 kg of Ayurvedic powder I at Rs. 40 per kg is mixed with 10 kg of an Ayurvedic powder II at Rs. 45 per kg. Find the average price of the Ayurvedic powder mixture.
In each of these questions two equations numbered (i) and (ii) are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer, if –
(i) 2p2 + 3p - 20 = 0
(ii) 2q² + 19q + 44 = 0
What should come in place of question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
401, 201,101, 51,?.
Direction∶ Study the following Bar Graph and answer the following questions.
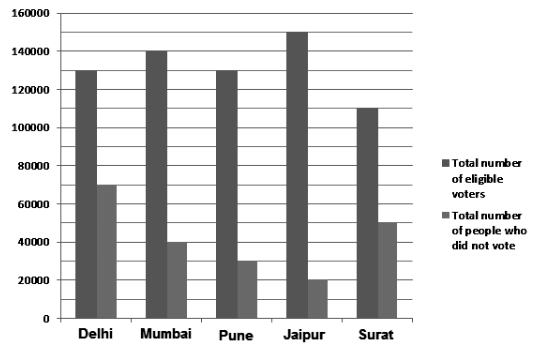
The Bar Graph shows the distribution of the total number of eligible voters and the total number of people who did not vote in 5 cities.
![]()
Q. Find the ratio of the minimum number of people who voted from these 5 cities to the maximum number of people who voted from these 5 cities.