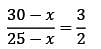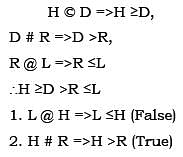Sikkim PCS Prelims Paper-II Mock Test- 2 - SPSC (Sikkim) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SPSC (Sikkim) Mock Test Series 2024 - Sikkim PCS Prelims Paper-II Mock Test- 2
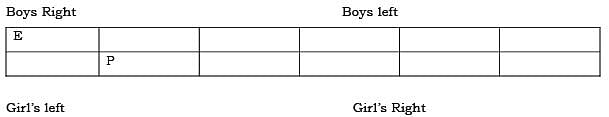
Six boys ABCDEF and six girls PQRSTU are standing in rows in such a way that each girl faces one boy, not necessarily in the same order.
- P is to the immediate right of the girl who is facing E the boy at the extreme right.
- Only B is sitting between D and E.
- F is to the immediate left of A and to the immediate right of C.
- R is facing A and is to the immediate left of Q.
- U is third to the left of S.
Which of the following girls is facing D?
Six boys ABCDEF and six girls PQRSTU are standing in rows in such a way that each girl faces one boy, not necessarily in the same order.
- P is to the immediate right of the girl who is facing E the boy at the extreme right.
- Only B is sitting between D and E.
- F is to the immediate left of A and to the immediate right of C.
- R is facing A and is to the immediate left of Q.
- U is third to the left of S.
Which of the following pairs of a boy and a girl is at one of the extreme ends?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Six boys ABCDEF and six girls PQRSTU are standing in rows in such a way that each girl faces one boy, not necessarily in the same order.
- P is to the immediate right of the girl who is facing E the boy at the extreme right.
- Only B is sitting between D and E.
- F is to the immediate left of A and to the immediate right of C.
- R is facing A and is to the immediate left of Q.
- U is third to the left of S.
Who is standing to the immediate left of D?
Six boys ABCDEF and six girls PQRSTU are standing in rows in such a way that each girl faces one boy, not necessarily in the same order.
- P is to the immediate right of the girl who is facing E the boy at the extreme right.
- Only B is sitting between D and E.
- F is to the immediate left of A and to the immediate right of C.
- R is facing A and is to the immediate left of Q.
- U is third to the left of S.
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
In a rare coin collection, there is one gold coin for every four non-gold coins. 5 more gold coins are added to the collection and the ratio of gold coins to non-gold coins would be 1: 3. Based on the information, the total number of coins in the collection now becomes
Ten new Magazines started on January, 5 Entertainment magazines, 3 political magazines 2 cricket magazines by April, only seven of the new magazines were still available, five of them being Entertainment magazines Based on the above information, four conclusions, as given below, have been made. Which one of these logically follows from the information given above?
Ram is younger to Harsh by 9 years. If their ages are in the respective ratio of 4:5, how old is Ram?
Shubh is 30 years old and Niku is 25 years old. How long ago was the ratio of their ages 3: 2?
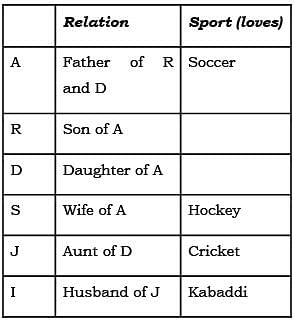
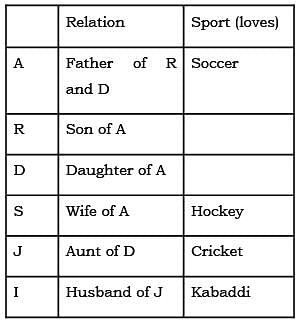
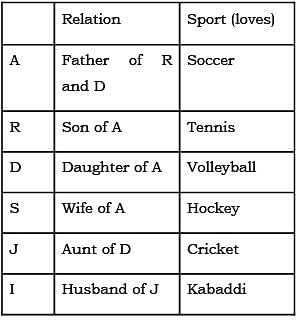
Direction for: A, R, D, S, J and I are 6 members of a family. There are two couples. Each loves a sport namely soccer, cricket, volleyball, tennis, hockey and kabaddi. A who loves soccer is father of R who does not loves volleyball and married to a woman who loves hockey, S is sister of J who loves cricket. D, the only daughter of A and her maternal Aunt J’s husband is I who loves kabaddi.
Q. How S related to D?
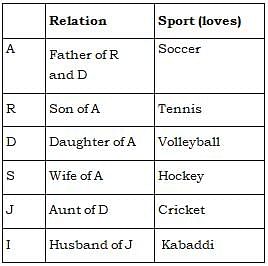
Direction: A, R, D, S, J and I are 6 members of a family. There are two couples. Each loves a sport namely soccer, cricket, volleyball, tennis, hockey and kabaddi. A who loves soccer is father of R who does not loves volleyball and married to a woman who loves hockey, S is sister of J who loves cricket. D, the only daughter of A and her maternal Aunt J’s husband is I who loves kabaddi.
Q. which sport R loves?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below.
A team of five is to be selected from amongst five boys A, B, C, D and E and four girls P, Q, R and S. Some criteria for selection are—
-
A and S have to be together
-
P cannot be put with R
-
D and Q cannot go together
-
C and E have to be together
-
R cannot be put with B
Unless otherwise stated, these criteria are applicable to all questions below.
Q. If two of the members have to be boys, the team will consist of—
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below.
A team of five is to be selected from amongst five boys A, B, C, D and E and four girls P, Q, R and S. Some criteria for selection are—
● A and S have to be together
● P cannot be put with R
● D and Q cannot go together
● C and E have to be together
● R cannot be put with B
Unless otherwise stated, these criteria are applicable to all questions below.
Q. If R be one of the members, the other members of the team are—
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below.
A team of five is to be selected from amongst five boys A, B, C, D and E and four girls P, Q, R and S. Some criteria for selection are—
A and S have to be together
P cannot be put with R
D and Q cannot go together
C and E have to be together
R cannot be put with B
Unless otherwise stated, these criteria are applicable to all questions below.
Q. If two of the members are girls and D is one of the members, the members of the team other than D are—
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below.
A team of five is to be selected from amongst five boys A, B, C, D and E and four girls P, Q, R and S. Some criteria for selection are—
A and S have to be together
P cannot be put with R
D and Q cannot go together
C and E have to be together
R cannot be put with B
Unless otherwise stated, these criteria are applicable to all questions below.
Q. If A and C are the members, the other members of the team cannot be—
Directions: Symbols @, %, #, $, ©
are used with different meanings as explained below:
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P % Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P $ Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
‘P © Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
Three statements showing relationships have been given, which are followed by two conclusions (1) and (2). Assuming that the given statements are true, find out which conclusions(s) is/are definitely true.
Q. Statements—H © D, D # R, R @ L. Conclusions—
L @ H
H # R
How many different words can be formed with the letter of the word DELHI. If these words begin with D and ends with H?
In a poor country like India, as income rises people first concentrate on increasing their consumption of what they regard as basic or more essential consumer goods. For the poor, these goods would primarily include cereals and for people at successive levels of higher income protective foods, simple non-food consumer goods, more modern, better quality non-food consumer goods and simple consumer durables, better quality consumer goods, and so on. When the demand for basic and more essential consumer goods is more or less met, demand for the next higher level of consumer goods begins to impinge on consumer decision making and their consumption increases. There is thus a hierarchy of income levels and a hierarchy of consumer goods. As incomes rise and one approaches the turning point referred to, there is an upward movement along the hierarchy in the demand for consumer goods which exhibits itself in a relative increase in the demand for these goods. If one examines the past consumption behaviour of households in India, one finds confirmation of the proposition just made. Until the mid seventies one notices a rise in the proportion of consumption expenditure on cereals, and thereafter, a steady decline reflecting a progressive increase in the relative expenditure on non-cereal or protective foods. About the same time the rising trend in the share of food in total consumption expenditure also begins to decline, raising the proportion of expenditure on non-food consumer goods. Simultaneously one also notices a sharper rise in the proportion of expenditure on consumer durables. Thus, what one sees is an upward movement in consumer demand along the hierarchy of consumer goods which amounts to a major change in consumer behaviour.
As income rises in a poor country like India, the poor people concentrate on increasing their consumption of
In a poor country like India, as income rises people first concentrate on increasing their consumption of what they regard as basic or more essential consumer goods. For the poor, these goods would primarily include cereals and for people at successive levels of higher income protective foods, simple non-food consumer goods, more modern, better quality non-food consumer goods and simple consumer durables, better quality consumer goods, and so on. When the demand for basic and more essential consumer goods is more or less met, demand for the next higher level of consumer goods begins to impinge on consumer decision making and their consumption increases. There is thus a hierarchy of income levels and a hierarchy of consumer goods. As incomes rise and one approaches the turning point referred to, there is an upward movement along the hierarchy in the demand for consumer goods which exhibits itself in a relative increase in the demand for these goods. If one examines the past consumption behaviour of households in India, one finds confirmation of the proposition just made. Until the mid seventies one notices a rise in the proportion of consumption expenditure on cereals, and thereafter, a steady decline reflecting a progressive increase in the relative expenditure on non-cereal or protective foods. About the same time the rising trend in the share of food in total consumption expenditure also begins to decline, raising the proportion of expenditure on non-food consumer goods. Simultaneously one also notices a sharper rise in the proportion of expenditure on consumer durables. Thus, what one sees is an upward movement in consumer demand along the hierarchy of consumer goods which amounts to a major change in consumer behaviour.
Whenever there is a decline in the proportion of consumption expenditure on cereals
In a poor country like India, as income rises people first concentrate on increasing their consumption of what they regard as basic or more essential consumer goods. For the poor, these goods would primarily include cereals and for people at successive levels of higher income protective foods, simple non-food consumer goods, more modern, better quality non-food consumer goods and simple consumer durables, better quality consumer goods, and so on. When the demand for basic and more essential consumer goods is more or less met, demand for the next higher level of consumer goods begins to impinge on consumer decision making and their consumption increases. There is thus a hierarchy of income levels and a hierarchy of consumer goods. As incomes rise and one approaches the turning point referred to, there is an upward movement along the hierarchy in the demand for consumer goods which exhibits itself in a relative increase in the demand for these goods. If one examines the past consumption behaviour of households in India, one finds confirmation of the proposition just made. Until the mid seventies one notices a rise in the proportion of consumption expenditure on cereals, and thereafter, a steady decline reflecting a progressive increase in the relative expenditure on non-cereal or protective foods. About the same time the rising trend in the share of food in total consumption expenditure also begins to decline, raising the proportion of expenditure on non-food consumer goods. Simultaneously one also notices a sharper rise in the proportion of expenditure on consumer durables. Thus, what one sees is an upward movement in consumer demand along the hierarchy of consumer goods which amounts to a major change in consumer behaviour.
Prices of protective food have risen because
It is an old saying that knowledge is power. Education is an instrument which imparts knowledge and, therefore, indirectly controls power. Therefore, ever since the dawn of civilization persons in power have always tried to supervise or control education. It has been the handmaid of the ruling class. During the Christian era, the ecclesiastics controlled the institution of education and diffused among the people the gospel of the Bible and religious teachings. These gospels and teachings were no other than a philosophy for the maintenance of the existing society. It taught the poor man to be meek and to earn his bread with the sweat of his brow, while the priests and the landlords lived in luxury and fought duels for the slightest offense.
Why have persons in power always tried to supervise or control education?
It is an old saying that knowledge is power. Education is an instrument which imparts knowledge and, therefore, indirectly controls power. Therefore, ever since the dawn of civilization persons in power have always tried to supervise or control education. It has been the handmaid of the ruling class. During the Christian era, the ecclesiastics controlled the institution of education and diffused among the people the gospel of the Bible and religious teachings. These gospels and teachings were no other than a philosophy for the maintenance of the existing society. It taught the poor man to be meek and to earn his bread with the sweat of his brow, while the priests and the landlords lived in luxury and fought duels for the slightest offense.
What do you mean by the “sweat of his brow”?
A wine seller had three types of wine. 435 litres of 1st kind, 609 litres of 2nd kind and 290 litres of 3rd kind. Find the least possible number of casks of equal size in which different types of wine can be filled without mixing.
The sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 11. If 45 is added to the number, then the digits are reversed. Find the number.
A watch which gains uniformly is 5 min slow at 7 pm on Monday and is 5 min 30 s fast at 7 pm on Friday. When was the watch correct?
Directions for the following 5 (five) questions:
The following pie charts gives regional distribution of candidates registered and passed in a competitive exam.
Q. A, B, C and D are four regions. Total 7200 students registered in exam and only 2400 passed in that. What is ratio of candidates passed from region C?
The following pie charts gives regional distribution of candidates registered and passed in a competitive exam.
Q. What is approximate percentage of candidates failed from region A?
The following pie charts gives regional distribution of candidates registered and passed in a competitive exam.
Q. Which region has highest success ratio?
The following pie charts gives regional distribution of candidates registered and passed in a competitive exam.
Q. What is ratio of the highest number of candidates successful from a region to lowest number of candidates appeared from a region?
The following pie charts gives regional distribution of candidates registered and passed in a competitive exam.
Q. What is overall percentage of candidates failed in exam?
Which property is illustrated by the equation (a + b) + c = c + (a + b) ?