EMRS TGT Maths Mock Test - 3 - EMRS MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test EMRS TGT Mock Test Series 2024 - EMRS TGT Maths Mock Test - 3
Van der Waal’s equation is related to which of the behaviour of which of the following?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Saturated carbon compounds can form which types of chain structures?
I. Straight chain
II. Branched-chain
Which of the cells of connective tissue secrete antibiotics?
Which is the first ever comic book launched by WWF-India ?
Which of the following properties are exhibited by the covalent compounds?
I. Have high boiling and melting point as compared to ionically bonded molecules
II. Are poor conductors of electricity.
III. Have weak inter-molecular force.
In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
B > C; C < D; D > E; E > F
Conclusions:
I. C < F
II. B > D
In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement:
P > S ≥ M = L < J = N
Conclusions:
I. L < N
II. P > M
III. S = L
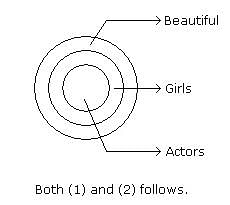
Statements:
All the actors are girls.
All the girls are beautiful.
Conclusions:
1. All the actors are beautiful.
2. Some girls are actors.
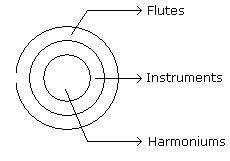
Statements:
All the harmoniums are instruments.
All the instruments are flutes.
Conclusions:
(1) All the flutes are instruments.
(2) All the harmoniums are flutes.
Kamali walks a distance of 3m towards North then turns to her left and walk for 2m.She turns left and walks for 3m.At this point she turns to his left and walk for 3m.How many metres is she from the starting point ?
One day afternoon Arun and Mani were sitting in a garden and facing each other.Mani’s shadow fall exactly towards Arun’s right, Which direction was Mani facing ?
P is 15m to the west of Q. R is 13m to the south of Q and 5m to the east of S. T is 20m to the north of S.T is 10m to the east of U…….
Q.
In which direction R with respect to P
N is more intelligent than M. M is not as intelligent as Y. X is more intelligent than Y but not as good as N. Who is the most intelligent of all ?
Q. In a queue, Rahul is fourteenth from the front and John is seventeenth from the end, while Alisha is in between Rahul and John. There are 48 persons in the queue, how many persons are there between Rahul and Alisha?
The _____________ enables you to simultaneously keep multiple web pages open in one browser window.
The following is not a part of the clinical method :
Confidential recording, scientific synthesis, and occupational therapy are the characteristics of :
Clinicians generally use two different procedures to develop case studies. One is clinical case study and the second one is :
A psychologist studied the individuals and compared the jobs they were employed in. Which method was he using :
Which of the following applies to the experimental method?
Appreciation, love and affection are part of the following needs of a child.
Which one of the following is not included by K Young (1947) as the needs occurring due to :
|
5 docs|20 tests
|