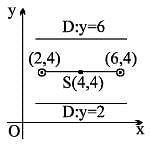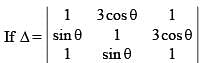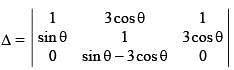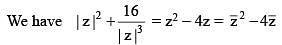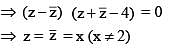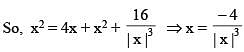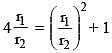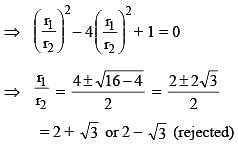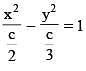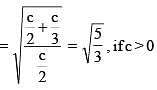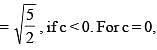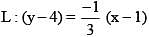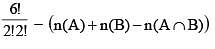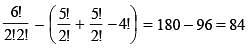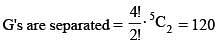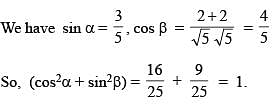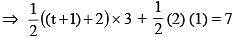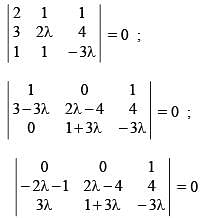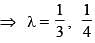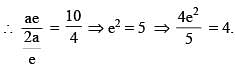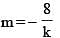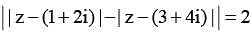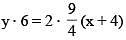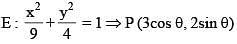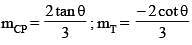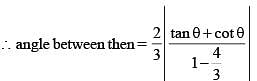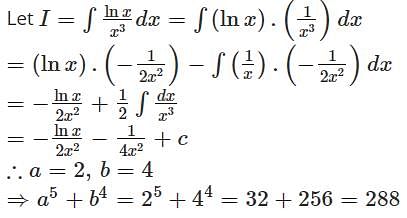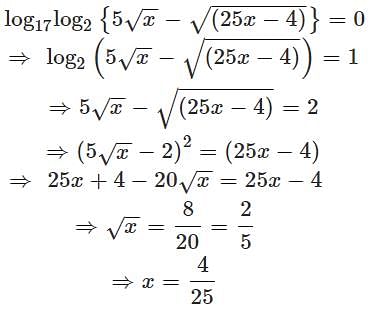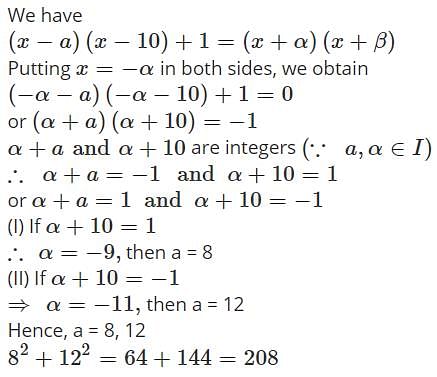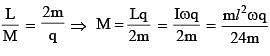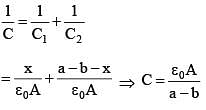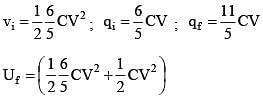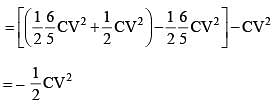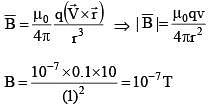JEE Main Practice Test- 15 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Practice Test- 15
The equation to the directrix of a parabola if the two extremities of its latus rectum are (2, 4) and (6, 4) and the parabola passes through the point (8, 1) is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The number of solution(s) of the equation
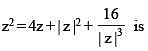
(where z = x + iy, x, y ∈ R, i2 = –1 and x ≠ 2)
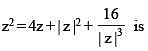
(where z = x + iy, x, y ∈ R, i2 = –1 and x ≠ 2)
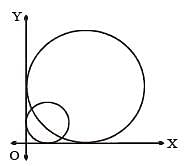
Two circles of radii r1 and r2 are both touching the coordinate axes and intersecting each other orthogonally. The value of r1/r2 (where r1 > r2) equals
Let X and Y be two matrices satisfying this relations
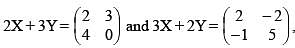
then Tr.(X) – Tr.(Y) equals
[Note : Tr.(P) denotes trace of matrix P.]
The differential equation dx/dy = 3y/2x represents a family of hyperbolas (except when it represents a pair of lines) with eccentricity can be
Line L, perpendicular to the line with equation y = 3x – 5, contains the point (1, 4). The x-intercept of L, is
Let A = [aij] (1 ≤ i , j ≤ 3) be a 3 × 3 matrix and B = [bij] (1 ≤ i , j ≤ 3) be a 3 × 3 matrix such that
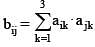
If det. A = 4, then the value of det. B is
Number of words that can be formed using all the letters of the word GARGEE if no two alike letters are together, is
If acute angle between the line 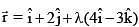 and xy plane is α and acute angle between the planes x + 2y = 0 and 2x + y = 0 is β then (cos2α + sin2β) equals
and xy plane is α and acute angle between the planes x + 2y = 0 and 2x + y = 0 is β then (cos2α + sin2β) equals
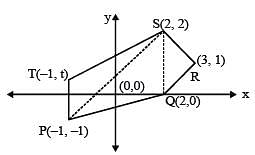
If area of pentagon PQRST be 7, where P(–1, –1), Q(2, 0), R(3, 1), S(2, 2) and T(–1, t), t > 0, then the value of t is
The sum of all value of λ for which the lines 2x + y + 1 = 0; 3x + 2λy + 4 = 0; x + y - 3λ = 0 are concurrent, is
If A and B are two independent events such that P(A' ∩ B') = 2/15, P(A ∩ B') = 1/6 then P(B) =
A hyperbola has centre at origin and one focus at (6, 8). If its two directrices are 3x + 4y + 10 = 0 and 3x + 4y –10 = 0 and eccentricity is e,then the value of 4e2/5 is equal to
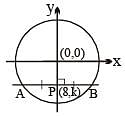
Number of integral values of 'k' for which the chord of the circle x2 + y2 = 125 passing through P(8, k) gets bisected at P (8, k) and has integral slope is
Locus of the feet of perpendiculars drawn from points (1, 2) and (3, 4) on a variable tangent to the conic | z - (1+ 2i) | - | z - (3+ 4i) | = 2 is
Number of numbers greater than a million and divisible by 5 which can be formed by using only the digits 1, 2,1, 2, 0, 5 and 2 is :
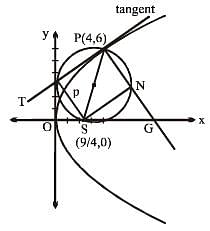
A normal is drawn to the parabola y2 = 9x at the point P(4, 6), S being the focus, a circle is described on the focal distance of the point P as diameter. The length of the intercept made by the circle on the normal at P is
Consider ellipse 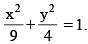 Let C is centre of the ellipse and P is a variable point lying on the ellipse. If the angle between CP and tangent at P is minimum, then P may be
Let C is centre of the ellipse and P is a variable point lying on the ellipse. If the angle between CP and tangent at P is minimum, then P may be
(Instruction to attempt numerical value (integer) type question: If your answer is 100 write 100 only. Do not write 100.0)
If 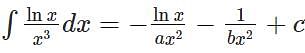 then the value of a5 + b4 must be
then the value of a5 + b4 must be
The sum of squares of all integral values of a for which the quadratic expression (x−a)(x−10)+1 can be factored as a product (x+α)(x+β) of two factors and α, β ∈ I must be equal to
If f(x) = tan-1 (sin x + cos x)3 is an increasing function, then the value of x in (0, 2π) is x ∈  Then the value of a + 10b + 100c + 1000d must be
Then the value of a + 10b + 100c + 1000d must be
The sum of two digit even numbers which do not end with zero is
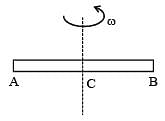
A non-conducting rod AB of length l has a total charge q. The rod is rotated about an axis passing through its center of mass with a constant angular velocity ω as shown in the figure. The magnetic moment of the rod is
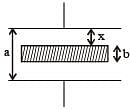
The distance between two parallel plates of a capacitor is a. A conductor of thickness b(b < a) is inserted between the plates as shown in the figure. The variation of effective capacitance between the plates of the capacitor as a function of the distance (x) is best represented by
A solid sphere of radius R, and dielectric constant ‘k’ has spherical cavity of radius R/4. A point charge q1 is placed in the cavity. Another charge q2 is placed outside the sphere at a distance of r from q1. Then Coulombic force of interaction between them is found to be ‘F1’. When the same charges are separated by same distance in vacuum then the force of interaction between them is found to be F2 then
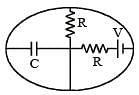
Energy stored in the capacitor in it’s steady state is
A point charge of 0.1C is placed on the circumference of a non-conducting ring of radius 1m which is rotating about an axis passing from centre and perpendicular to the plane of ring with a constant angular acceleration of 1 rad/sec2. If ring starts from rest at t = 0, the magnetic field at the centre of the ring at t = 10 sec, is