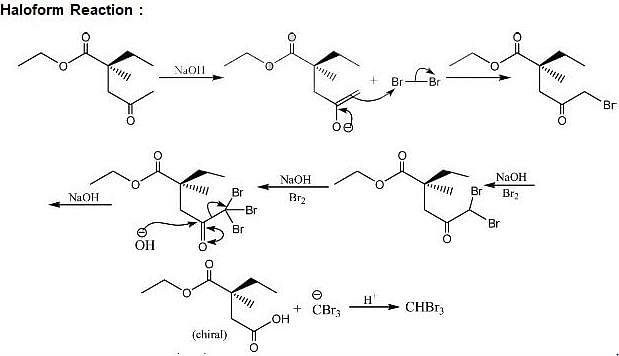
Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 3 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry - Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 3
For the reaction below if the concentration of KCN is increased four times, the rate of the reaction will be:
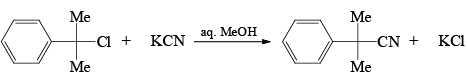
The major product formed in the reaction of 1, 3-butadiene with bromine is at high temperature:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The products formed in the following reaction is:
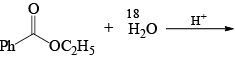
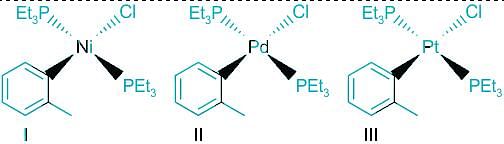
The order of rate of substitution of chloride by pyridine (in ethanol) in the following complexes
The major product formed in the following reaction.
The major product formed in the following reaction.
The major product obtained in the following reaction
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Choose the correct order of reactivity for dehydration of the given alcoho ls using concentrated sulfuric acid.
Electrophilic nitrations of the following compounds follow the trend:
The set of products formed in the following reaction is:
What would be the final major product of the following chemical reaction if it is carried out twice, one at 5 Co and the second time at 45 C0?
What is the major product if HBr (in excess) is added to H2C = CH – CH2 – OH
The reaction of sodium ethoxide with ethyl iodide to form diethyl ether is termed
What is the final product after the following reaction has gone to completion?
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Among the bro mides I-III given below, the order of their reactivity in the SN1 reaction is:
The major product formed in the reaction benzoic acid with isobutylene in the presence of a catalytic amount of sulfuric acid is:
Among the following compounds, the one that undergoes deprotonation most readily in the presence of a base, to form a carbanion is:
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|