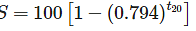Practice Test: Civil Engineering (CE)- 8 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Practice Test: Civil Engineering (CE)- 8
Select the pair that does not expresses a relationship similar to that expressed in the pair:
Wheel: spokes
If a, b and c are three positive integers such that a and b are in the ratio 3:4 while b and c are in the ratio 2:1, then minimum integer value of a + b + c is _________
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Reaching a place of appointment of Friday. I found that I was two days earlier than the scheduled day. If I had reached on the following Wednesday then how many days late would I have been?
Which of the following options is the closest in the meaning to the word given below?
Impeccable
Choose the most appropriate word(s) from the options given below to complete the following sentence.
It was hoped at the time that that place would become the centre from which the civilization of Africa would proceed; but this ________ was not fulfilled.
3, k, 2, 8, m, 3
The arithmetic mean of the list of numbers above is 4. If k and m are integers and k ≠ m, what is the median of the list?
Consider a random walk on an infinite two-dimensional triangular lattice, a part of which is shown in the figure below.
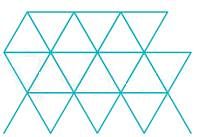
If the probabilities of moving to any of the nearest neighbour sites are equal. What is the probability that the walker returns to the starting position at the end of exactly three steps?
Twelve straight lines are drawn in a plane such that no two of them are parallel and no three of them are concurrent. A circle is now drawn in the same plane such that all the points of intersection of all the lines lie inside the circle. What is the number of non-overlapping regions into which the circle is divided?
Electromagnetic radiation is an insidious culprit. Once upon a time, the major concern around electromagnetic radiation was due to high tension wires which carry huge amounts of electricity to cities. Now, we even carry sources of this radiation with us as cell phones, laptops, tablets and other wireless devices. While the most acute exposures to harmful levels of electromagnetic radiation are immediately realized as burns, the health effects due to chronic or occupational exposure may not manifest effects for months or years.
Which of the following can be the viable solution for electromagnetic radiation reduction?
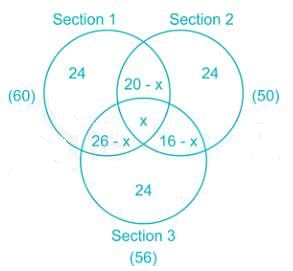
In a mock exam, there were 3 sections. Out of all students, 60 students cleared the cut off in section 1, 50 students cleared the cutoff in section 2 and 56 students cleared the cut off in section 3. 20 students cleared the cutoff in section 1 and section 2, 16 cleared cut off in section 2 & section 3, 26 cleared the cut off in section 1 & section 3. The number of students who cleared cutoff of the only one section was equal & was 24 for each section. How many students cleared cut off all the three sections?
Let f(z) = z̅ and g(z) = |z|2 for all ϵ C. Then at z = 0.
The probability density function of a random variable X is given by

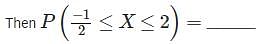
 represents the parabola, then the value of m will be?
represents the parabola, then the value of m will be?
The non-zero of n for which the differential equation (3xy2 + n2 x2y) dx + (nx3 + 3x2y) dy = 0, x ≠ 0 become exact differential equation is:
The normal duration and normal cost of an activity are 25 days and 50,000 rupees respectively. The activity crash duration is 22 days and the indirect cost is 1000 rupees per day. If the cost slope is 1500 rupees per day, then the crash cost of the activity will be
Which one of the following is incorrect?
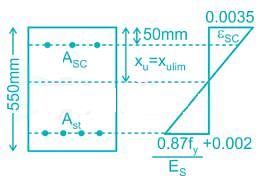
A doubly reinforced concrete beam with effective cover of 50 mm to centre of both tension and compression reinforcement with effective depth of 550 mm. If the maximum permissible stress in the outermost fibres in both steel and concrete reaches at the same time, what will be the maximum strain in concrete at the level of compression reinforcement satisfying codal provisions of IS 456:2000 according to limit state method.
Take Fe 500 grade of steel for both tension and compression reinforcement and M 20 grade of concrete.
A close box subjected to the following loading conditions as shown in figure below. The ratio of distribution factor for the member AB to member BC is?
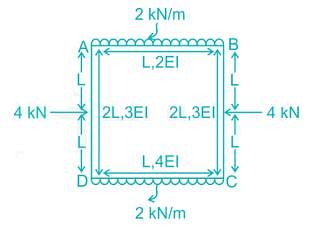
Clear distance between lateral restrains for continuous reinforced concrete beam of size 250 × 500 mm (effective depth) according to IS 456:2000 shall be limited to:
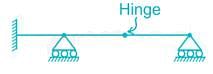
The number of independent degrees of freedom for the beam shown below is
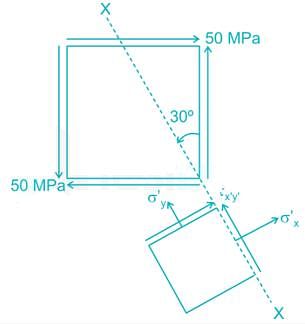
A state of pure shear is shown in figure below. What will be the radius and centre of moh’r circle at x – x shown in figure below

A transmission tower carries a vertical load of 10000 kg, the vertical stress increment at a depth 6 m directly below the tower as per Boussinesq’s theory is____Pa.
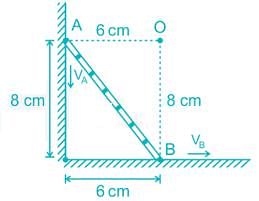
For a ladder shown in figure, the velocity of point A is 0.2 m/min in vertically downward direction the velocity of point B in horizontally rightward direction will be ____ m/s.

If the liquid limit and plastic limit of the soil is observed as 60% and 45% respectively and the percentage by weight of particles finer than 2μ is 30%, then identify the correct option:
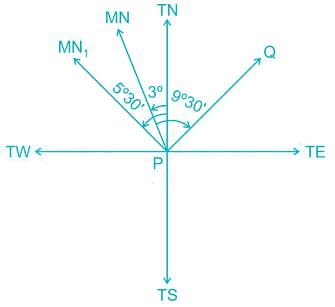
If in an old map the line PQ was drawn to a magnetic bearing of 9° 30’ and the magnetic declination at the time being 3° West. If the present magnetic declination is 5° 30’ West, then the present magnetic bearing of the line PQ will be?
The ratio of Discharge in prototype (Qp) to the Discharge in model (Qm) for a geometrically. Similar model of spillway is 35000, the scale of the model used is 1 in ______.
If the velocity components in 2 – Dimensional incompressible fluid flow is represented as 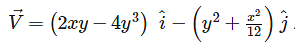 Find the rate of shear strain in (x – y) plane.
Find the rate of shear strain in (x – y) plane.
A wastewater is incubated for 8 days and the BOD8 at 20°C is found to be 250 mg/L. The ratio of oxygen available in the wastewater to the total oxygen required to satisfy its first stage BOD demand expressed as the percentage of total oxygen required will be ____ %.
|
31 docs|280 tests
|
|
31 docs|280 tests
|


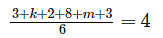



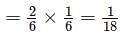

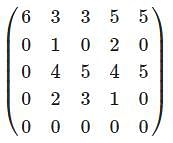
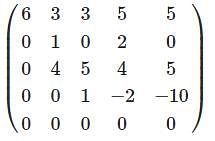
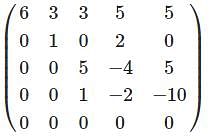
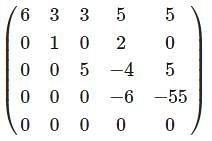
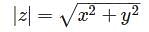


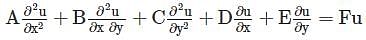
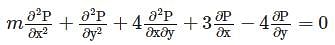
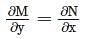
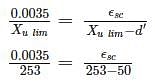
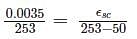

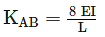
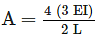
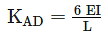
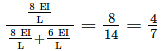
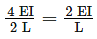


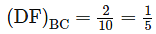
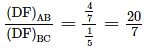
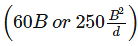 whichever is lesser
whichever is lesser  = 31250mm = 31.25m
= 31250mm = 31.25m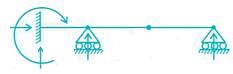

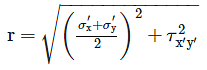

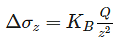

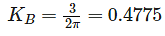



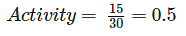

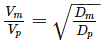
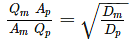
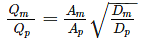
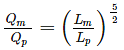
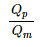 = 35000
= 35000 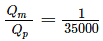
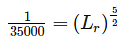
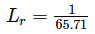
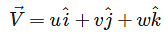

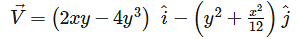
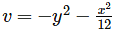

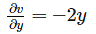
 (OK, flow is possible)
(OK, flow is possible)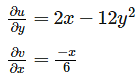
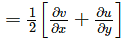

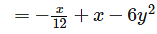 =
=