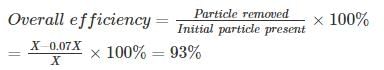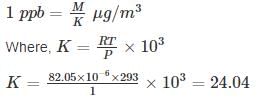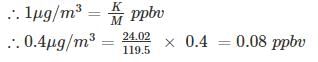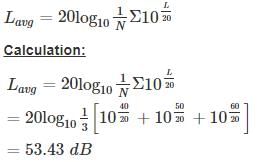Test: Environmental Engineering- 6 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Environmental Engineering- 6
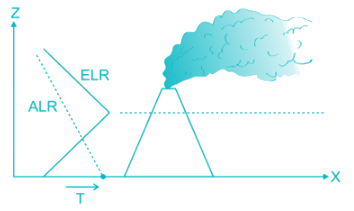
Which kind of plume has minimum downward mixing as its downward motion is prevented by inversion and upward mixing will be quite turbulent and rapid?
According to the Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000, of the Ministry of Environment Forests, India, the day time and night time noise level limits in ambient air for residential area expressed in dB (A) Leq are
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
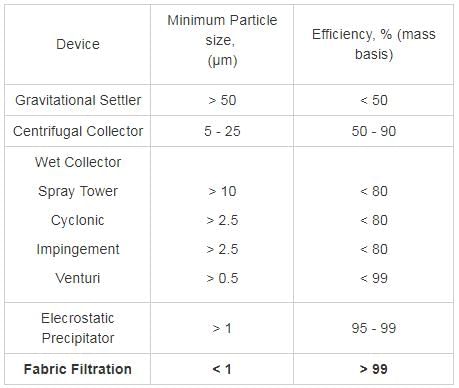
Which of the following engineering system for air pollution control device can collect a particle size of less than one micrometer and can also have an efficiency as high as 99%
An air parcel having 40° temperature moves from ground level to 500m elevation in dry air following the “adiabatic lapse rate”. The temperature of air parcel at 500 m elevation will be
Arrange the layers of the atmosphere in order of increasing heights from the surface of the earth
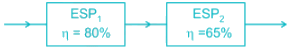
Two electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are in series. The fractional efficiencies of upstream and downstream ESPs for size dp are 80% and 65% respectively.
What is the overall efficiency of the system for the same dp?
Assuming annual travel for each vehicle to be 50000 km, the quantity of NOx produced from 200,000 vehicle with emission rate 2.5 gm/km/vehicle is
The mean indoor airborne chloroform (CHCl3) concentration in a room was determined to be 0.4 µg/m3. Use the following data:
T = 293 K
P = 1 atmosphere
R = 82.05 × 10-6 atm.m3/mol-K
Atomic weights: C = 12, H = 1, Cl = 35.5. The concentration expressed in parts per billion (volume basis, ppbv) is equal to –
At a location three sound pressure levels were recorded as 40 dB, 50 dB, & 60 dB. The average sound pressure level is ________
|
31 docs|280 tests
|
|
31 docs|280 tests
|