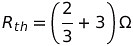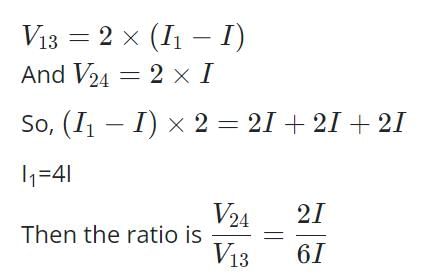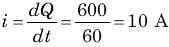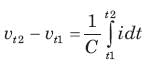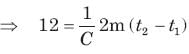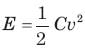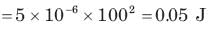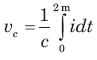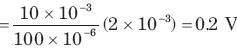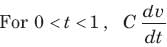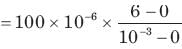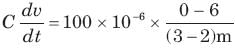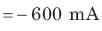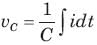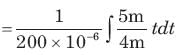Test: Basic Concepts of Network Theory - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Basic Concepts of Network Theory
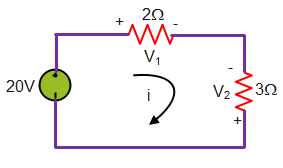
For the circuit given below.
What is the value of V2?

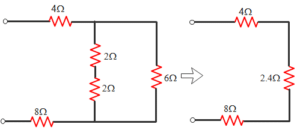
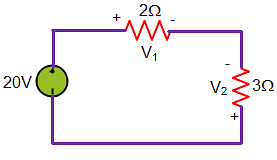
For the circuit given below.
What is the value of equivalent resistance?

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
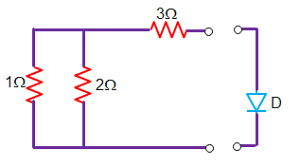
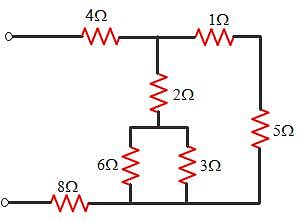
The circuit given below.The Thevenin resistance across the diode in the circuit is?
The Thevenin resistance across the diode in the circuit is?

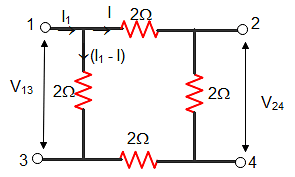
Consider the following circuit.
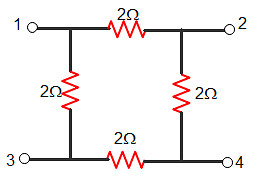
What is the value of V24 / V13 of given circuit?
In the circuit given, a charge of 600 C is delivered to the 100 V source in a 1 minute. The value of v1 must be:
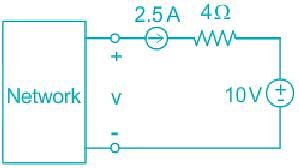
In the circuit of the fig the value of the voltage source E is:
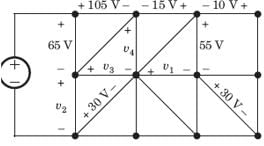
Consider the circuit graph shown in fig. Each branch of circuit graph represent a circuit element. The value of voltage v1 is:
What quantity of charge must be delivered by a battery with a Potential Difference of 110 V to do 660J of Work?
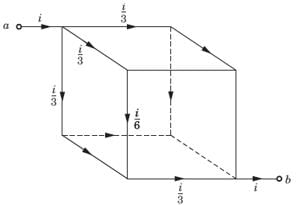
Twelve 6 Ω resistor are used as edge to form a cube.The resistance between two diagonally opposite corner of the cube is
In a AC circuit, resistive and total impedance are 10 and 20 ohms respectively. What is the phase angle difference between the voltage and current?
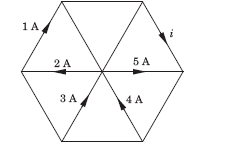
The quantity of a charge that will be transferred by a current flow of 10 A over 1 hour period is _________ ?
A capacitor is charged by a constant current of 2 mA and results in a voltage increase of 12 V in a 10 sec interval. The value of capacitance is:
The energy required to charge a 10 μF capacitor to 100 V is:
The current in a 100 μF capacitor is shown in fig. If capacitor is initially uncharged, then the waveform for the voltage across it is:
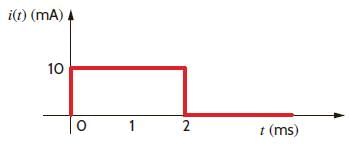
The voltage across a 100 μF capacitor is shown in fig. The waveform for the current in the capacitor is:
The waveform for the current in a 200 μF capacitor is shown in fig. The waveform for the capacitor voltage is:
|
25 docs|263 tests
|
|
25 docs|263 tests
|