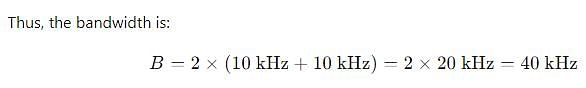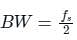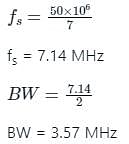Test: Electromagnetic & Analog Communications - 2 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Electromagnetic & Analog Communications - 2
If r2 = x2 + y2 + z2 then the value of 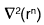 is
is
The potential (scalar) distribution is V = 10y4 + 20x3. If ∈0 be the permittivity of free space, then the charge density 'p' at the point (0, 2) is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The skin depth of copper at a frequency of 3 GHz is 1 micron (10-6 meter). At 12 GHz for a non-magnetic conductor whose conductivity is 1/9 times that of copper, the skindepth would be
Shortest length of a 42 Ω air line required toproduce a reactance of j73Ω at 1 MHz when line is short circuited is
A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50Ω is terminated by a resistor 100Ω.
Q. The impedance at the voltage maximum position is
A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50Ω is terminated by a resistor 100Ω.
Q. The impedance at the voltage minimum position is
An EM wave travels in free space with the electric field component, E. = 100 ei(a866 + a5z)ax V/m and ω = 3 x 108 rad/sec. The time average power in the wave is
A 50Ω characteristic impedance line is connected to a load which shows a reflection coefficient of 0.268. If Vin = 15 V, then the net power delivered to the load will be
A TEM wave impinges obliquely on a dielectric-dielectric boundary (,
). The angle of incidence for total reflection is
Match List-I (Nature of Polarization) with
List-II (Relationship Between X and Y components) for a propagating wave having cross-section in the XY plane and propagating along Z-direction and select the correct answer:
List-I
A. Linear
B. Left circular
C. Right circular
D. Elliptical
List-II
-
X and Y components are in same phase
-
X and Y components have arbitrary phase difference
- component leads Y by 90°
- X component lags behind Y by 90°
Consider the following statements:
- FDM is possible when the useful bandwidth of the medium exceeds the required bandwidth of signals to be transmitted.
- Synchronous TDM is not possible when the achievable data rate of the medium exceeds the data rate of digital signals to be transmitted.
A 1 kHz sinusoidal signal is ideally sampled at 1400 samples/sec and the sampled signal is passed through an ideal low-pass filter with cut-off frequency 800 Hz. The output signal has the frequency kHz
In a SSB modulation, the power spectral density of m(t) is given as

where a and W are constants. White Gaussian noise of zero mean and PSD of N0/2 is added to SSB modulator wave at the receiver input. The (SNR) at the output of the receiver is,
(Where Ac = Carrier signal amplitude)
An angle modulated signal with carrier frequency ωc = 2π x 105 is described by the equation QAm (t) = 10 cos (ωc t + 5 sin 3000 t + 10 sin 2000 πt)
The maximum frequency deviation is
A frequency modulated wave is 100% modulated by 10 kHz modulating signal m(t). Then the bandwidth required is
A sinusoid x(t) = A cos2πfot is sampled at 5 times the Nyquist rate for 2.5 sec. A total of 250 samples are acquired value of fs and fm are given by
The angle-modulated signal with carrier frequency ωc = 27c x 106 is discribed by the equation
v(t) = 10 cos(ωct + 10sin200t + 20si n400πt) The deviation ratio is
A PCM system uses a uniform quantizer followed by a 7-bit binary encoder. The bit rate of the system is equal to 50 x 106 bps.
Q. The maximum message bandwidth for which the system oeprates satisfactorily, is
The approximate output signal - to (quantization) noise ratio when a full - load sinusoidal modulating wave of frequency 1 MHz is applied to the input, is
For an AM wave, the maximum voltage was found to be 10 V and the minimum voltage was found to be 5 V. The modulation index of the wave would be
|
25 docs|263 tests
|
|
25 docs|263 tests
|