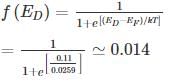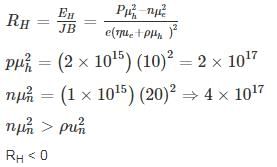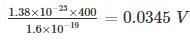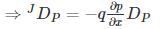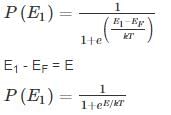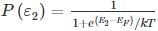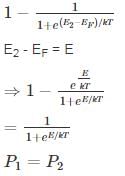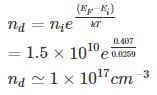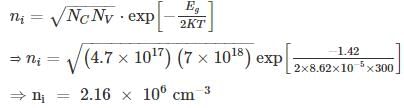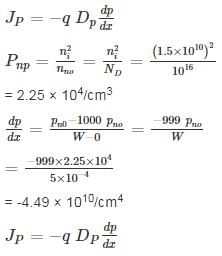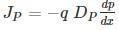Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Electronic Devices - 2
Which of the following quantities cannot be measured/determined using Hall Effect?
The ratio of hole diffusion current to the electron diffusion current in an infinite p-n junction is 4. If conductivity on p-side is 1.4 S/cm and on n-side is 2.8 S/cm, then the ratio of diffusion length Ln and Lp (ie Ln/Lp) is _______.
Under high electric fields, in a semiconductor with increasing electric field,
The energy band structure of n-type semiconductor is as shown below
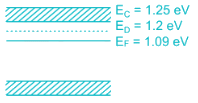
The probability that the donor energy state is empty is (up to 3 significant digits)
In a hypothetical semiconductor hole concentration is 2 × 1015/cm3 and electron concentration is 1 × 1015/cm3. The mobility of holes is 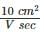 and mobility of electrons is
and mobility of electrons is 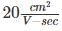
If the specimen is subjected to hall measurement. Then the measured hall coefficient (RH) is
In a germanium semiconductor at 127°C has a hole concentration gradient between two points 1.5 × 1022/m3. If the hole mobility in germanium is 800 cm2/v-s, then the diffusion current density is ______ A/m2.
2 Consider two energy levels: E1, E eV above the Fermi level and E2, EeV below the Fermi level. P1 and P2 are respectively the probabilities of E1 being occupied by an electron and E2 being empty. Then
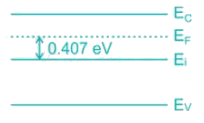
A silicon sample is dope with unknown concentration of Arsenic, such that the fermi level (EF) is 0.407 eV relative to intrinsic level (Ei). The conductivity of the silicon sample after doping is______(Ω – cm)-1.
The mobility of electrons μn = 3800 cm2/v-s and holes μp = 1800 cm2/v-s. Take kT = 0.0259 eV at 300°K and intrinsic concentration ni = 1.5 × 1010 cm-3
The effective density of states in conduction and valence band NC and Nv at 300K is 4.7x1017 cm−3 and 7x1018cm−3 respectively. The bandgap of the mentioned semiconductor is 1.42eV at 300K. The intrinsic carrier concentration is:
Use Boltzmann constant k = 8.62 x 10−5 eV/K
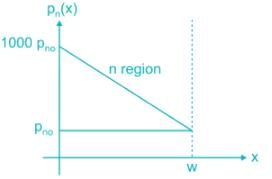
Holes are being steadily injected into a region of n-type silicon. In the steady state, the excess hole concentration profile is shown. [The term excess means over and above concentrations pno]
If Dp = 12 cm2/sec ND = 1016/cm3, ni = 1.5 × 1010/cm3 and w = 5 μm.
The current density that will flow in x-direction is _____ nA/cm2.
|
26 docs|263 tests
|


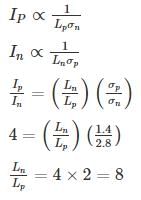

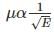 when 103 < E < 104 V/cm
when 103 < E < 104 V/cm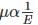 when E > 104 V/cm
when E > 104 V/cm