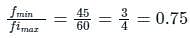Test: Phase Modulation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Phase Modulation
Which of the following phase modulation applications is INCORRECT?
In the phase modulated signal, the deviation of frequency is ________.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
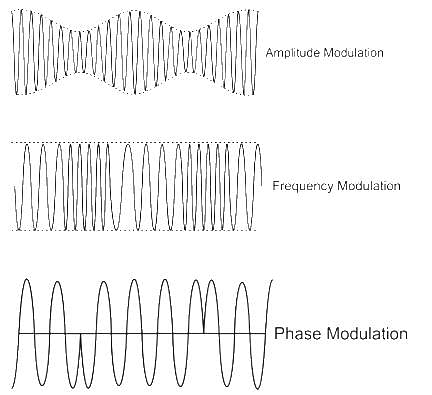
Phase modulation is generally not used for transmission because
In which of the following, the phase of the carrier wave changes in accordance with the intensity of light.
An angle modulated signal with carrier frequency ωc = 2π × 106 rad/s given by ϕm(t) = cos(ωct + 5 sin (1000πt) + 10 sin (2000πt)). The maximum deviation of the frequency in the angle modulated signal from that of the carrier is ___________ kHz.
A phase modulated signal can be obtained from frequency modulator by passing the modulating signal through a
In phase modulated signal, the frequency deviation is proportional to
A message signal m(t) = Am sin (2πfmt) is used to modulate the phase of a carrier Ac cos (2πfct) to get the modulated signal y(t) = Ac cos (2πfct + m(t)). The bandwidth of y(t)
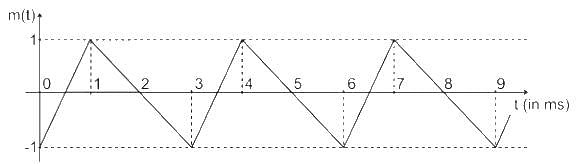
The baseband signal m(t) shown in the figure is phase-modulated to generate the PM signal φ(t) = cos(2πfct + km(t)). The time t on the x-axis in the figure is in milliseconds. If the carrier frequency fc = 50 kHz and k = 10π, then the ratio of the minimum instantaneous frequency (in kHz) to the maximum instantaneous frequency (in kHz) is __________ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
|
25 docs|263 tests
|
|
25 docs|263 tests
|


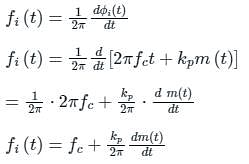
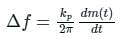
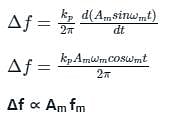
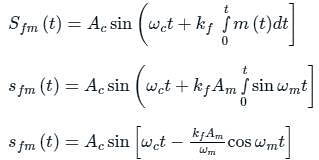
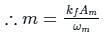
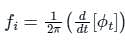
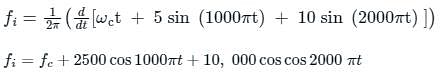
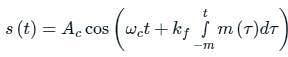
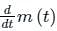 as the input to the frequency modulator, i.e.
as the input to the frequency modulator, i.e.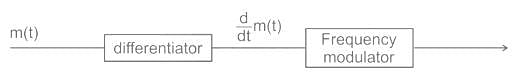
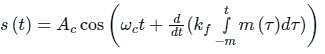
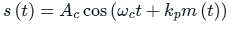
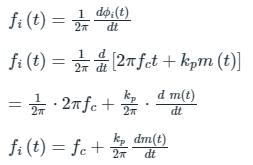
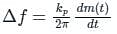
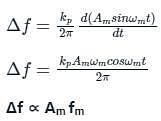
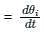
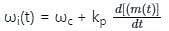
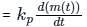
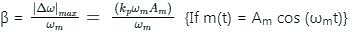
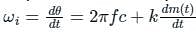 if θ (t) = 2π fct + k m(t)
if θ (t) = 2π fct + k m(t)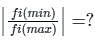
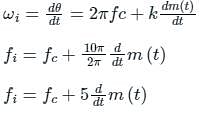
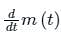 is the slope of the message signal:
is the slope of the message signal: