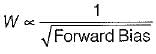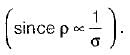Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Tests > GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 > Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Semiconductor Diodes
Test: Semiconductor Diodes for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 preparation. The Test: Semiconductor Diodes questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus.The Test: Semiconductor Diodes MCQs are made for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Semiconductor Diodes below.
Solutions of Test: Semiconductor Diodes questions in English are available as part of our GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) & Test: Semiconductor Diodes solutions in
Hindi for GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Semiconductor Diodes | 10 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2025 for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 1
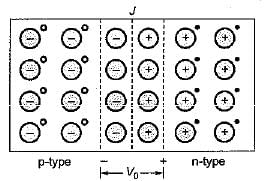
The barrier voltage (V0 or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect of
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 3
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 4
The most commonly used type of electron emission in electron tubes is
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 5
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 6
The emission of electrons in a vacuum diode is achieved by
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 7
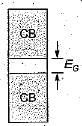
The main reason why electrons can tunnel through a p-n junction is that
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 8
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 9
The barrier voltage for germanium is _________ at 25°C.
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 9
Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 10
With the increase in temperature, the resistivity of an intrinsic semiconductor decreases. This is because, with the increase of temperature
Detailed Solution for Test: Semiconductor Diodes - Question 10
|
25 docs|263 tests
|
Information about Test: Semiconductor Diodes Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Semiconductor Diodes solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Semiconductor Diodes, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
25 docs|263 tests
|
Download as PDF