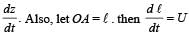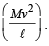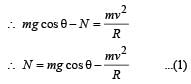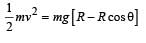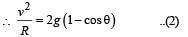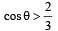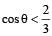Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Laws of Motion | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
6 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Laws of Motion | JEE Advanced
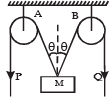
In the arrangement shown in the Fig, the ends P and Q of an unstretchable string move downwards with uniform speed U. Pulleys A and B are fixed.
Mass M moves upwards with a speed

A reference frame attached to the earth
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
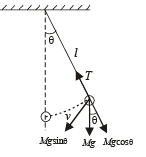
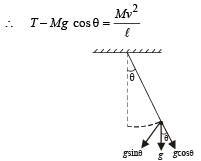
A simple pen dulum of length L an d mass (bob) M is oscillating in a plane about a vertical line between angular limit – φ and + φ . For an angular displacement θ (|θ| < φ), the tension in the string and the velocity of the bob are T and V respectively. The following relations hold good under the above conditions :
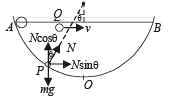
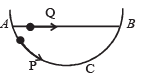
A particle P is sliding down a frictionless hemispherical bowl.
It passes the point A at t = 0. At this instant of time, the horizontal component of its velocity is v. A bead Q of the same mass as P is ejected from A at t = 0 along the horizontal string AB, with the speed v. Friction between the bead and the string may be neglected. Let tP and tQ be the respective times taken by P and Q to reach the point B. Then :
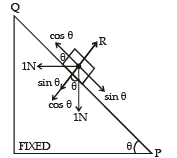
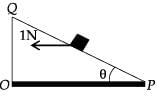
A small block of mass of 0.1 kg lies on a fixed inclined plane PQ which makes an angle θ with the horizontal. A horizontal force of 1 N acts on the block through its centre of mass as shown in the figure.
The block remains stationary if (take g = 10 m/s2)
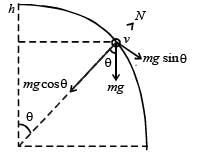
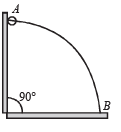
A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the form of quarter of a circle. The wire is fixed vertically on ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire and it slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from A to B, the force it applies on the wire is
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|