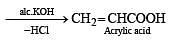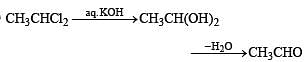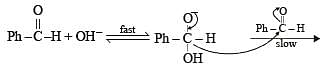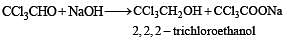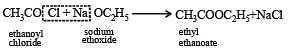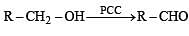Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids
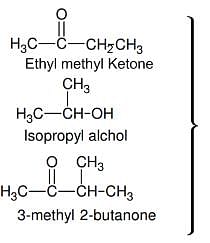
On vigorous oxidation by permanganate solution.
(CH3)2C = CH - CH2 - CHO gives
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Picric acid is:
When CH2 = CH — COOH is reduced with LiAlH4, the compound obtained will be
On mixing ethyl acetate with aqueous sodium chloride, the composition of the resultant solution is
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl gives
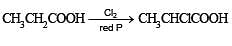
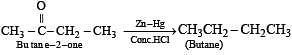
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?
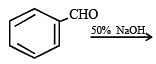
Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% sodium hyroxide solution to give the corresponding alcohol and acid?
Among the following acids which has the lowest pKa value?
Reaction of cycloh exan on e with dimethylamine in th e presence of catalytic amount of an acid forms a compound if water during the reaction is continuously removed. The compound formed is generally known as
The increasing order of the rate of HCN addition to compound A – D is
(A) HCHO
(B) CH3COCH3
(C) PhCOCH3
(D) PhCOPh
The correct order of increasing acid strength of the compounds
(A) CH3CO2H
(B) MeOCH2CO2H
(C) CF3CO2H
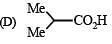
is
A liquid was mixed with ethanol and a drop of concentrated H2SO4 was added. A compound with a fruity smell was formed. The liquid was :
Which of the following on heating with aqueous KOH, produces acetaldehyde?
In Cannizzaro reaction given below
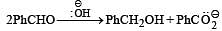
the slowest step is :
Which of the following reagents may be used to distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid?
Trichloroacetaldehyde was subjected to Cannizzar o’s reaction by using NaOH. The mixture of the products contains sodium trichloroacetate and another compound.
The other compound is :
The strongest acid amongst the following compounds is :
Sodium ethoxide has reacted with ethanoyl chloride. The compound that is produced in the above reaction is :
Silver Mirror test is given by which one of the following compounds?
Iodoform can be prepared from all except :
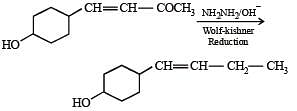
In the given transformation, which of the following is the most appropriate reagent ?

The most suitable reagent for the conversion of R - CH2 - OH → R- CHO is:
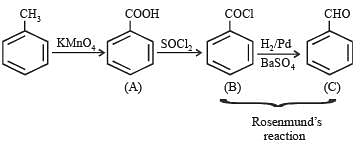
In the reaction,
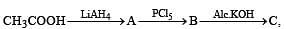
the product C is:
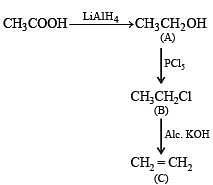
In the following sequence of reactions :
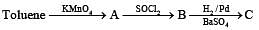
the product C is :
|
446 docs|930 tests
|
|
446 docs|930 tests
|


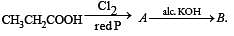 What is B?
What is B?