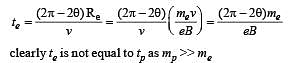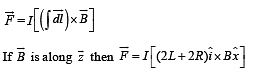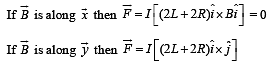Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Moving Charges & Magnetism | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Moving Charges & Magnetism | JEE Advanced
A magnetic needle is kept in a non uniform magnetic field. It experiences
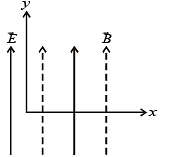
A proton moving with a constant velocity passes through a region of space without any change in its velocity. If E and B represent the electric and magnetic fields respectively, this region of space may have :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A rectangular loop carrying a current i is situated near a long straight wire such that the wire is parallel to one of the sides of the loop and is in the plane of the loop. If steady current I is established in the wire as shown in the figure, the loop will :

Two thin long parallel wires seperated by a distance ‘b’ are carrying a current ‘i’ amp each. The magnitude of the force per unit lenght exerted by one wire on the other is
Two particles X and Y having equal charges, after being accelerated through the same potential difference, enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is
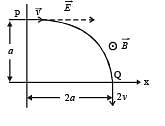
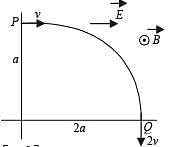
A particle of charge + q and mass m moving under the influence of a uniform electric field Eiˆ and uniform magnetic field B kˆ follows a trajectory from P to Q as shown in fig. The velocities at P and Q are viˆ and – 2vˆj . Which of the following statement (s) is/are correct ?
A microameter has a resistance of 100 W and a full scale range of 50 mA . It can be used as a voltmeter or as a higher range ammeter provided a resistance is added to it. Pick the correct range and resistance combination (s)
A current I flows along the length of an infinitely long, straight, thin-walled pipe. Then
H+, He+ and O++ all having the same kinetic energy pass through a region in which there is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to their velocity. The masses of H+, He+ and O2+ are 1 amu, 4 amu and 16 amu respectively. Then
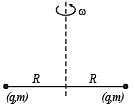
Two particles, each of mass m and charge q, are attached to the two ends of a light rigid rod of length 2R. The rod is rotated at constant angular speed about a pependicular axis passing through its centre. The ratio of the magnitudes of the magnetic moment of the system and its angular momentum about the centre of the rod is
Two very long, straight, parallel wires carry steady currents I & -I respectively. The distance between the wires is d. At a certain instant of time, a point charge q is at a point equidistant from the two wires, in the plane of the wires. Its instantaneous velocity v is perpendicular to this plane. The magnitude of the force due to the magnetic field acting on the charge at this instant is
The following field line can never represent
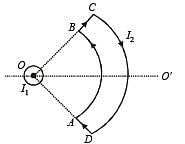
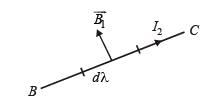
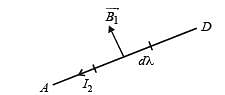
A long current carrying wire, carrying current I1 such that I1 is flowing out from the plane of paper is placed at O. A steady state current I2 is flowing in the loop ABCD
A particle of mass m and charge q, moving with velocity v enters Region II normal to the boundary as shown in the figure. Region II has a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the paper. The length of the Region II is l Choose the correct choice(s).
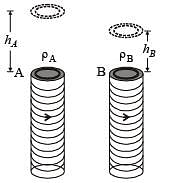
Two metallic rings A and B, identical in shape and size but having different resistivities ρA and ρB, are kept on top of two identical solenoids as shown in the figure. When current I is switched on in both the solenoids in identical manner, the rings A and B jump to heights hA and hB, respectively, with hA > hB. The possible relation(s) between their resistivities and their masses mA and mB is(are)
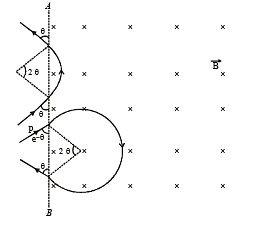
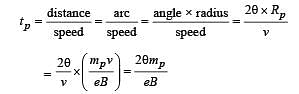
An electron and a proton are moving on straight parallel paths with same velocity. They enter a semi infinite region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the velocity. Which of the following statement(s) is / are true?
Consider the motion of a positive point charge in a region where there are simultaneous uniform electric and magnetic fields 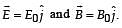 At time t = 0, this charge has velocity
At time t = 0, this charge has velocity  the in the x-y plane, making an angle θ with the x-axis. Which of the following option(s) is (are) correct for time t > 0?
the in the x-y plane, making an angle θ with the x-axis. Which of the following option(s) is (are) correct for time t > 0?
A particle of mass M and positive charge Q, moving with a constant velocity  enters a region of uniform static magnetic field, normal to the x-y plane. The region of the magnetic field extends from x = 0 to x = L for all values of y. After passing through this region, the particle emerges on the other side after 10 milliseconds with a velocity
enters a region of uniform static magnetic field, normal to the x-y plane. The region of the magnetic field extends from x = 0 to x = L for all values of y. After passing through this region, the particle emerges on the other side after 10 milliseconds with a velocity  . The correct statement(s) is (are)
. The correct statement(s) is (are)
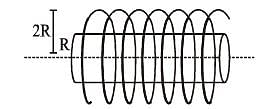
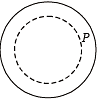
A steady current I flows along an infinitely long hollow cylindrical conductor of radius R. This cylinder is placed coaxially inside an infinite solenoid of radius 2R. The solenoid has n turns per unit length and carries a steady current I. Consider a point P at a distance r from the common axis. The correct statement(s) is (are)
A conductor (shown in the figure) carrying constant current I is kept in the x-y plane in a uniform magnetic field r B . If F is the magnitude of the total magnetic force acting on the conductor, then the correct statement(s) is(are)
Consider two identical galvanometers and two identical resistors with resistance R. If the internal resistance of the galvanometers RC < R/2, which of the following statement(s) about any one of the galvanometers is (are) true?
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|


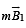
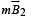
 where r is the distance between the wires. Therefore, there will be a net attractive force on the rectangular loop. Force on BC is equal and opposite to that on AD.
where r is the distance between the wires. Therefore, there will be a net attractive force on the rectangular loop. Force on BC is equal and opposite to that on AD.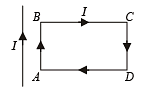
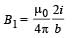
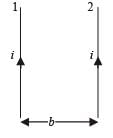
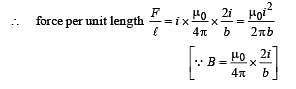
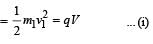
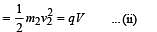
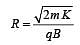

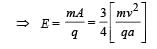
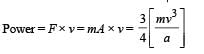
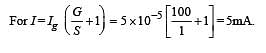
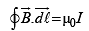
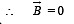
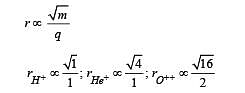
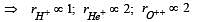
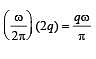
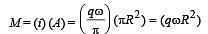
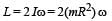 .
.
 and
and  is 180°,
is 180°,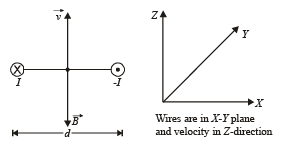

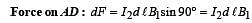
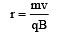
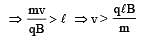
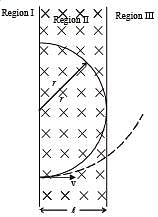
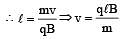
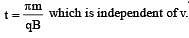
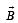 is present on the right hand side of AB. The electron (e) and proton (p) moving on straight parallel paths with the same velocity enter the region of uniform magnetic field.
is present on the right hand side of AB. The electron (e) and proton (p) moving on straight parallel paths with the same velocity enter the region of uniform magnetic field.