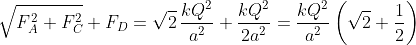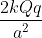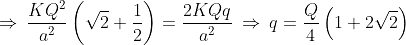Test: Electric Charges and Fields - 2 - CUET Humanities MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Agriculture Practice Tests: CUET Preparation - Test: Electric Charges and Fields - 2
Two small identical balls P and Q, each of mass √3/10 grams, carry identical charges and are suspended by threads of equal length. At equilibrium, they position themselves as shown in the figure. What is the charge on each ball?
Given: (1/4πε0) = 9  109 Nm2C-2 and g = 10 ms-2
109 Nm2C-2 and g = 10 ms-2

Given: (1/4πε0) = 9

An infinite number of charges, each equal to q, are placed along the x-axis at x = 1, x = 2, x = 4, x = 8, and so on. If the consecutive charges have opposite signs, then the electric field at x = 0 would be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two point charges, q and 4q are held a distance 'r' apart. The electric field due to them is zero at a distance
If the inward flux and outward electric flux from a closed surface respectively are 8 × 103 units and 4 × 103 units, then what is the net charge inside the closed surface?
There is a uniform electric field of strength 103 Vm–1 along the y-axis. A body of mass 1 g and charge 10–6 C is projected into the field from the origin along the positive x-axis with a velocity of 10 ms–1. Its speed (in ms–1) after 10 seconds will be (neglect gravitation)
A glass rod rubbed with fur is brought near the cap of a negatively charged gold leaf electroscope (glass rod will be negatively charged). The leaf divergence will
The electric field due to an extremely short dipole at a distance r from it is proportional to
Three point charges +q, -q and +q are respectively placed at the vertices P, Q and R of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. If F = where r is the side of the triangle, then the force on charge at P due to charges at Q and R is
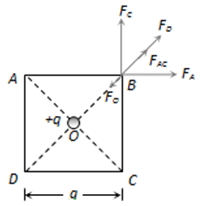
Four charges equal to -Q are placed at the four corners of a square and a charge q is at its centre. If the system is in equilibrium, the value of q is
A metallic spherical shell of radius R has a charge –Q distributed uniformly on it. A point charge +Q is placed at the centre of the shell. Which of the following graphs represents the variation of electric field E with distance r from the centre of the shell?
A pith ball carrying a charge 1 nC is suspended by an insulated thread of length 50 cm. When a uniform electric field is applied in a horizontal direction, the ball is found to deflect by 2 cm from the vertical. If the mass of the ball is 0.5 g, then what is the magnitude of the electric field and the angle made by the thread with the vertical?
If a charged body attracts another charged body, the charge on the other body
Electric field lines emanating from a charge q are shown in the figure. What is the sign of the charge q?

Two plastic straws are rubbed with a silk cloth. Which of the following statements is/are true?
- The straws will repel each other.
- The straws will attract the silk cloth.
- The straws will repel the silk cloth.
- The straws will attract each other.
When a charged rod is brought near the electroscope, the leaves of the electroscope move apart. It means the rod is



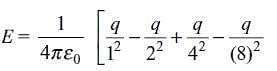
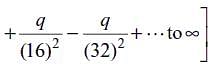
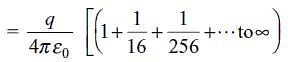
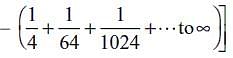
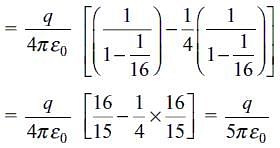
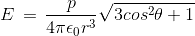
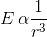 .
.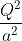 towards AB
towards AB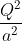 towards CB
towards CB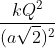 towards DB
towards DB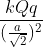 towards BO
towards BO