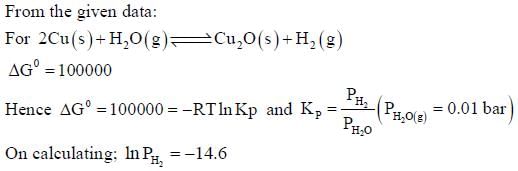JEE (Advanced) 2018 Paper - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test National Level Test Series for JEE Advanced 2025 - JEE (Advanced) 2018 Paper - 2
A particle of mass m is initially at rest at the origin. It is subjected to a force and starts moving along the x-axis. It's kinetic energy K changes with time as dK/dt = γt, where γ is a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. Which of the following statements is (are) true?
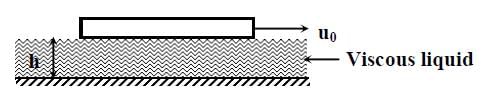
Consider a thin square plate floating on a viscous liquid in a large tank. The height h of the liquid in the tank is much less than the width of the tank. The floating plate is pulled horizontally with a constant velocity u0. Which of the following statements is (are) true?
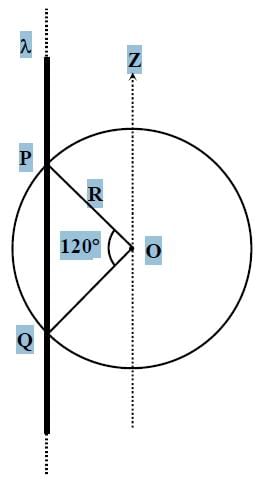
An infinitely long thin non-conducting wire is parallel to the z-axis and carries a uniform line charge density λ. It pierces a thin nonconducting spherical shell of radius R in such a way that the arc PQ subtends an angle 120° at the centre O of the spherical shell, as shown in the figure. The permittivity of free space is ε0. Which of the following statements is (are) true?

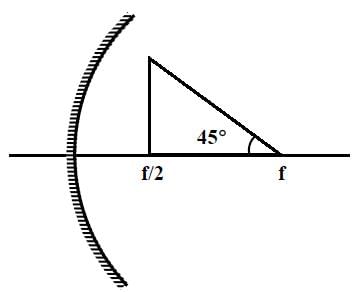
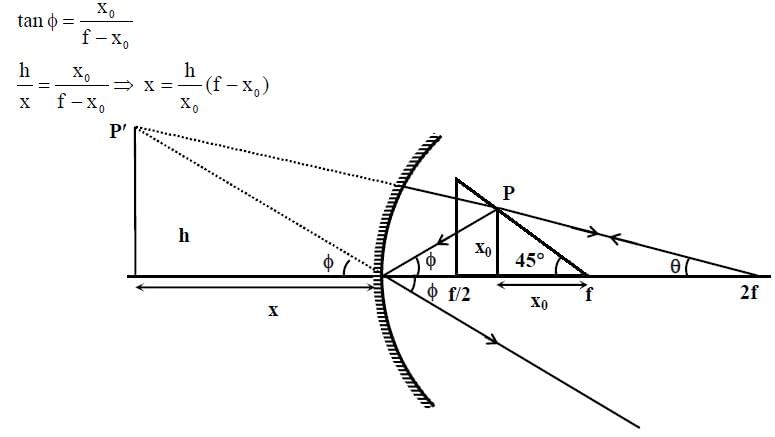
A wire is bent in the shape of a right angled triangle and is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length f, as shown in the figure. Which of the figures shown in the four options qualitatively represent(s) the shape of the image of the bent wire? (These figures are not to scale.)
In a radioactive decay chain, 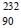 Th nucleus decays to
Th nucleus decays to  Pb nucleus. Let Nα and Nβ be the number of α and β- particles, respectively, emitted in this decay process. Which of the following statements is (are) true?
Pb nucleus. Let Nα and Nβ be the number of α and β- particles, respectively, emitted in this decay process. Which of the following statements is (are) true?
In an experiment to measure the speed of sound by a resonating air column, a tuning fork of frequency 500 Hz is used. The length of the air column is varied by changing the level of water in the resonance tube. Two successive resonances are heard at air columns of length 50.7 cm and 83.9 cm. Which of the following statements is (are) true?
A solid horizontal surface is covered with a thin layer of oil. A rectangular block of mass m = 0.4 kg is at rest on this surface. An impulse of 1.0 Ns is applied to the block at time t = 0 so that it starts moving along the x-axis with a velocity v(t) = 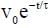 , where v0 is a constant and
, where v0 is a constant and 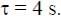 The displacement of the block, in meters, at
The displacement of the block, in meters, at 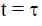 is _________. Take e-1 = 0.37.
is _________. Take e-1 = 0.37.
A ball is projected from the ground at an angle of 45° with the horizontal surface. It reaches a maximum height of 120 m and returns to the ground. Upon hitting the ground for the first time, it loses half of its kinetic energy. Immediately after the bounce, the velocity of the ball makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal surface. The maximum height it reaches after the bounce, in metres, is ___________.
A particle, of mass 10-3 kg and charge 1.0 C, is initially at rest. At time t = 0, the particle comes under the influence of an electric field 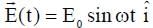 , where E0 = 1.0 NC-1 and ω = 103 rad s-1 . Consider the effect of only the electrical force on the particle. Then the maximum speed, in m s-1, attained by the particle at subsequent times is ____________.
, where E0 = 1.0 NC-1 and ω = 103 rad s-1 . Consider the effect of only the electrical force on the particle. Then the maximum speed, in m s-1, attained by the particle at subsequent times is ____________.
A moving coil galvanometer has 50 turns and each turn has an area 2 x 10-4 m2. The magnetic field produced by the magnet inside the galvanometer is 0.02 T. The torsional constant of the suspension wire is 10-4 N m rad-1. When a current flows through the galvanometer, a full-scale deflection occurs if the coil rotates by 0.2 rad. The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer is 50 Ω. This galvanometer is to be converted into an ammeter capable of measuring current in the range 0 - 1.0 A. For this purpose, a shunt resistance is to be added in parallel to the galvanometer. The value of this shunt resistance, in ohms, is __________.
A steel wire of diameter 0.5 mm and Young’s modulus 2 x 1011 Nm-2 carries a load of mass M. The length of the wire with the load is 1.0 m. A vernier scale with 10 divisions is attached to the end of this wire. Next to the steel wire is a reference wire to which a main scale, of least count 1.0 mm, is attached. The 10 divisions of the vernier scale correspond to 9 divisions of the main scale. Initially, the zero of vernier scale coincides with the zero of main scale. If the load on the steel wire is increased by 1.2 kg, the vernier scale division which coincides with a main scale division is __________. Take g = 10 ms-2 and is π = 3.2.
One mole of a monatomic ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion in which its volume becomes eight times its initial value. If the initial temperature of the gas is 100 K and the universal gas constant R = 8.0 J mol-1K-1, the decrease in its internal energy, in Joule, is__________.
In a photoelectric experiment a parallel beam of monochromatic light with power of 200 W is incident on a perfectly absorbing cathode of work function 6.25 eV. The frequency of light is just above the threshold frequency so that the photoelectrons are emitted with negligible kinetic energy. Assume that the photoelectron emission efficiency is 100%. A potential difference of 500 V is applied between the cathode and the anode. All the emitted electrons are incident normally on the anode and are absorbed. The anode experiences a force F = n x 10-4 N due to the impact of the electrons. The value of n is __________. Mass of the electron me = 9 x 10-31 kg and 1.0 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J.
Consider a hydrogen-like ionized atom with atomic number Z with a single electron. In the emission spectrum of this atom, the photon emitted in the n = 2 to n = 1 transition has energy 74.8 eV higher than the photon emitted in the n = 3 to n = 2 transition. The ionization energy of the hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV. The value of Z is __________.
The electric field E is measured at a point P(0, 0, d) generated due to various charge distributions and the dependence of E on d is found to be different for different charge distributions. List-I contains different relations between E and d. List-II describes different electric charge distributions, along with their locations. Match the functions in List-I with the related charge distributions in List-II.

A planet of mass M, has two natural satellites with masses m1 and m2. The radii of their circular orbits are
R1 and R2 respectively. Ignore the gravitational force between the satellites. Define v1, L1, K1 and T1 to be,
respectively, the orbital speed, angular momentum, kinetic energy and time period of revolution of satellite
1; and v2, L2, K2 and T2 to be the corresponding quantities of satellite 2. Given m1/m2 = 2 and R1/R2 = 1/4,
match the ratios in List-I to the numbers in List-II.

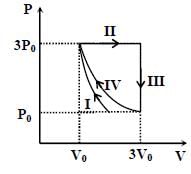
One mole of a monatomic ideal gas undergoes four thermodynamic processes as shown schematically in the PVdiagram below. Among these four processes, one is isobaric, one is isochoric, one is isothermal and one is adiabatic. Match the processes mentioned in List-1 with the corresponding statements in List-II.

In the List-I below, four different paths of a particle are given as functions of time. In these functions, α and β are positive constants of appropriate dimensions and  . In each case, the force acting on the particle is either zero or conservative. In List-II, five physical quantities of the particle are mentioned:
. In each case, the force acting on the particle is either zero or conservative. In List-II, five physical quantities of the particle are mentioned:  the linear momentum,
the linear momentum, 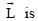 the angular momentum about the origin, K is the kinetic energy, U is the potential energy and E is the total energy. Match each path in List-I with those quantities in List-II, which are conserved for that path.
the angular momentum about the origin, K is the kinetic energy, U is the potential energy and E is the total energy. Match each path in List-I with those quantities in List-II, which are conserved for that path.
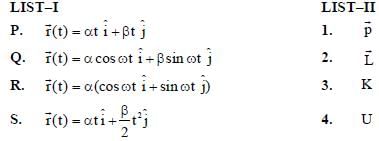
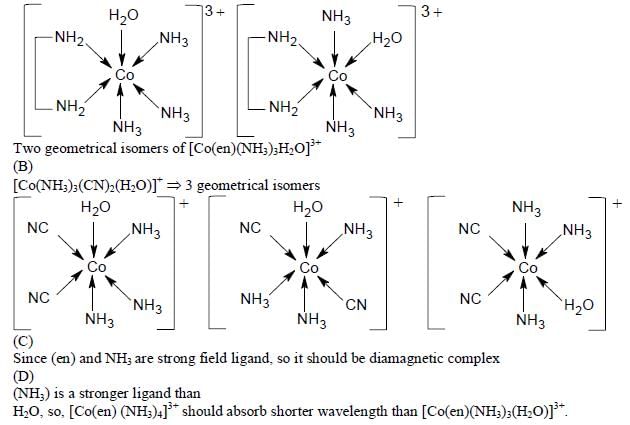
The correct option(s) regarding the complex 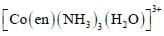 (en = H2NCH2CH2NH2) is (are)
(en = H2NCH2CH2NH2) is (are)
The correct option(s) to distinguish nitrate salts of Mn2+ and Cu2+ taken separately is (are)
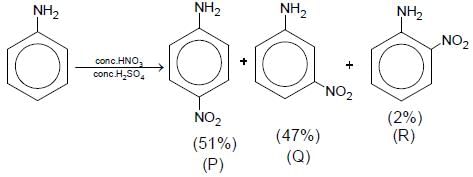
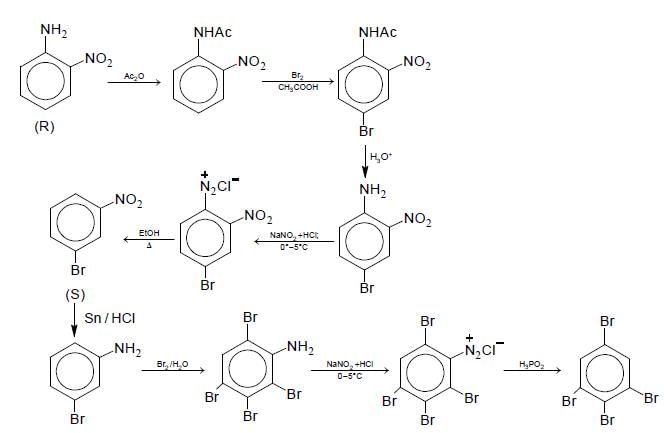
Aniline reacts with mixed acid (conc. HNO3 and conc. H2SO4) at 288 K to give P (51%), Q (47%) and R(2%). The major product(s) of the following reaction sequence is (are)
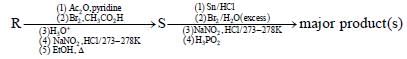
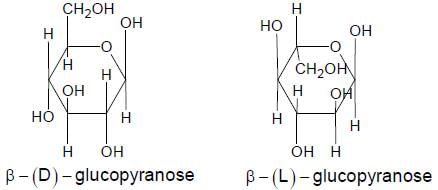
The Fischer presentation of D-glucose is given below
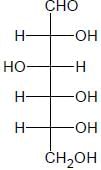
D-glucose
The correct structures(s) of β - L-glucopyranose is(are)
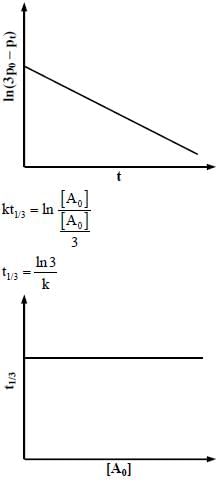
For a first order reaction A(g) → 2B(g) + C(g) at constant volume and 300 K, the total pressure at the beginning (t = 0) and at time t are Po and Pt, respectively. Initially, only A is present with concentration [A]0, and 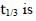 the time required for the partial pressure of A to reach 1/3rd of its initial value. The correct option(s) is (are) (Assume that all these gases behave as ideal gases)
the time required for the partial pressure of A to reach 1/3rd of its initial value. The correct option(s) is (are) (Assume that all these gases behave as ideal gases)
For a reaction, A ⇌ P, the plots of [A] and [P] with time at temperatures T1 and T2 are given below.
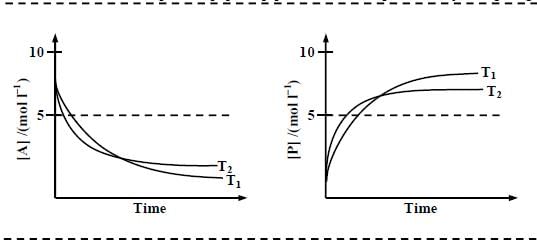
If T2 > T1, the correct statement(s) is (are) (Assume ΔHθ and ΔSθ are independent of temperature and ratio
of lnK at T1 to lnK at T2 is greater than T2/T1. Here H, S, G and K are enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs energy and
equilibrium constant, respectively.)
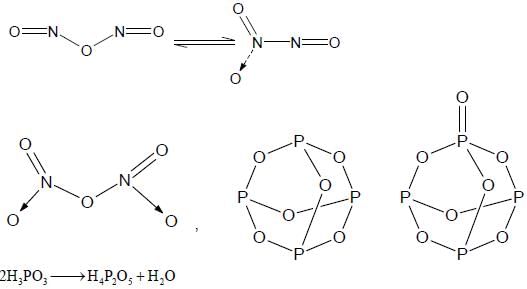
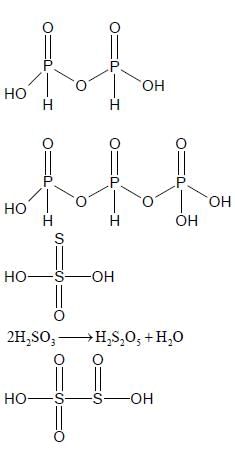
The total number of compounds having at least one bridging oxo group among the molecules given below
is ____.
N2O3, N2O5, P4O6, P4O7, H4P2O5, H5P3O10, H2S2O3, H2S2O5
Galena (an ore) is partially oxidized by passing air through it at high temperature. After some time, the
passage of air is stopped, but the heating is continued in a closed furnace such that the contents undergo
self-reduction. The weight (in kg) of Pb produced per kg of O2 consumed is ____.
(Atomic weights in g mol-1: O = 16, S = 32, Pb = 207)
To measure the quantity of MnCl2 dissolved in an aqueous solution, it was completely converted to KMnO4
using the reaction, MnCl2 + K2S2O8 + H2O -->KMnO4 + H2SO4 + HCl (equation not balanced). Few drops
of concentrated HCl were added to this solution and gently warmed. Further, oxalic acid (225 mg) was
added in portions till the colour of the permanganate ion disappeared. The quantity of MnCl2 (in mg)
present in the initial solution is ____.
(Atomic weights in g mol−1: Mn = 55, Cl = 35.5)
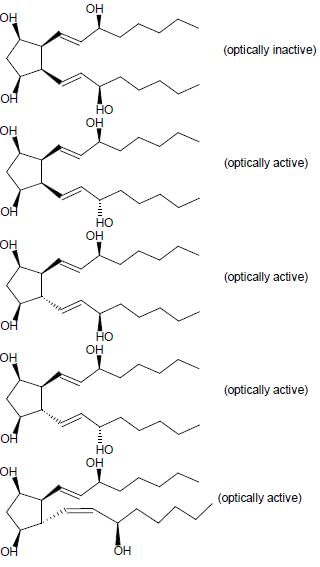
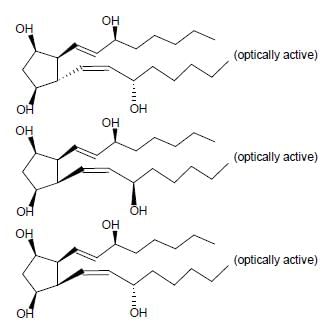
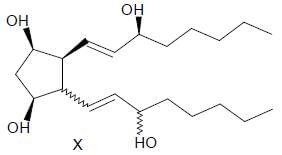
For the given compound X, the total number of optically active stereoisomers is ____

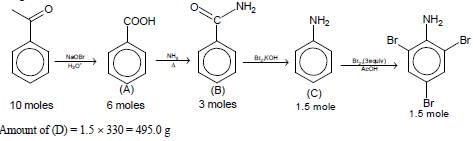
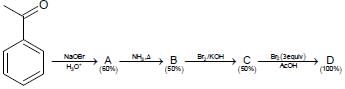
In the following reaction sequence, the amount of D (in g) formed from 10 moles of acetophenone is ____.
(Atomic weights in g mol–1: H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O = 16, Br = 80. The yield (%) corresponding to the
product in each step is given in the parenthesis)
The surface of copper gets tarnished by the formation of copper oxide. N2 gas was passed to prevent the
oxide formation during heating of copper at 1250 K. However, the N2 gas contains 1 mole % of water
vapour as impurity. The water vapour oxidises copper as per the reaction given below:
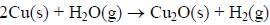
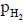 is the minimum partial pressure of H2 (in bar) needed to prevent the oxidation at 1250 K. The value of
is the minimum partial pressure of H2 (in bar) needed to prevent the oxidation at 1250 K. The value of
ln 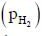 is ____.
is ____.
(Given: total pressure = 1 bar, R (universal gas constant) = 8 J K-1 mol-1, ln(10) = 2.3. Cu(s) and Cu2O(s)
are mutually immiscible.
At 1250 K: 2Cu(s) + ½ O2(g) --> Cu2O(s); ΔGθ = − 78,000 J mol−1
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) --> H2O(g); ΔGθ = − 1,78,000 J mol−1; G is the Gibbs energy)
|
3 videos|2 docs|40 tests
|
|
3 videos|2 docs|40 tests
|


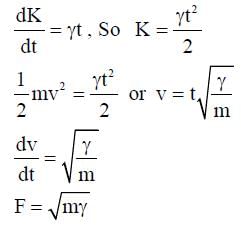

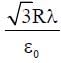
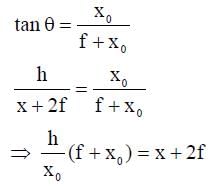
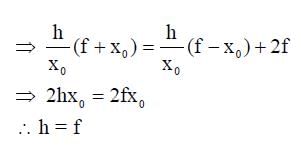
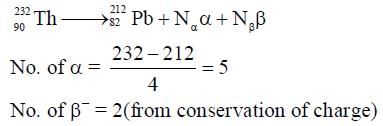


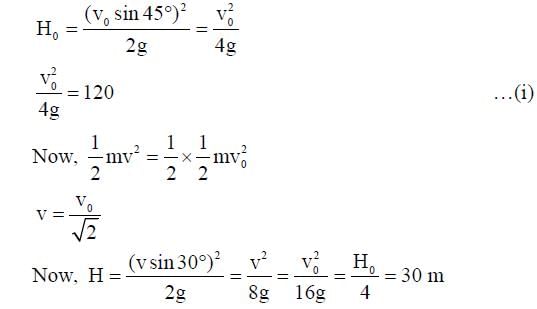
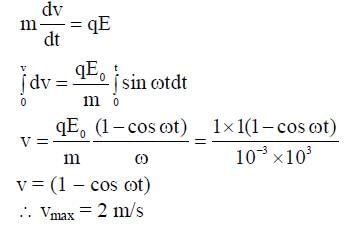
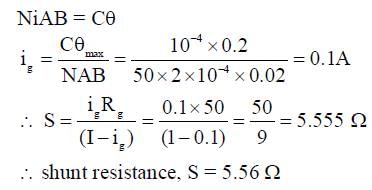

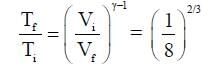
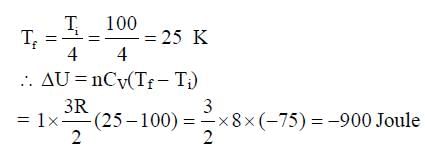
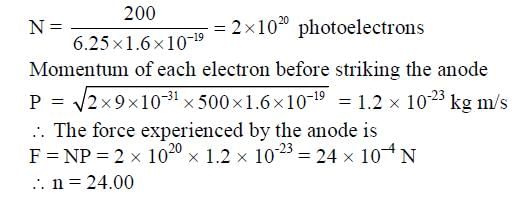
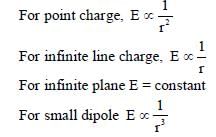

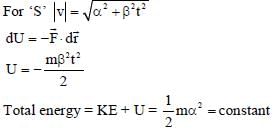
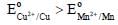
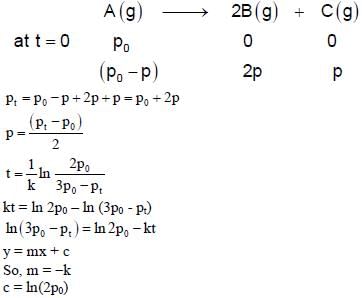

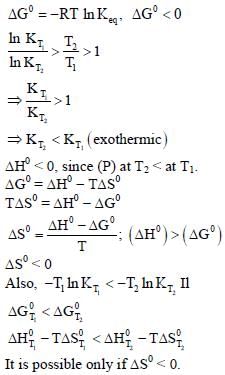

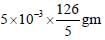 = 126 mg
= 126 mg