JEE Advanced 2014 Paper -1 with Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test National Level Test Series for JEE Advanced 2025 - JEE Advanced 2014 Paper -1 with Solutions
Q. 1 - 10 carry 3 marks each.
Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
A student is performing an experiment using a resonance column and a tuning fork of frequency
244s-1 . He is told that the air in the tube has been replaced by another gas (assume that the column remains filled with the gas). If the minimum height at which resonance occurs is (0.350 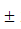 0.005)m , the gas in the tube is
0.005)m , the gas in the tube is
(Useful information:  The molar masses M in grams are given in the options. Take the values of
The molar masses M in grams are given in the options. Take the values of 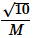 for each gas as given there.)
for each gas as given there.)
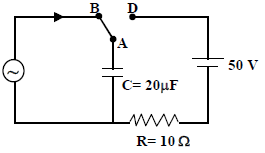
At time t = 0, terminal A in the circuit shown in the figure is connected to B by a key and an alternating
current I(t) = I0 cos (ωt), with I0 = 1A and ω = 500 rad/s starts flowing in it with the initial direction shown
in the figure. At 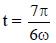 the key is switched from B to D. Now onwards only A and D are connected. A
the key is switched from B to D. Now onwards only A and D are connected. A
total charge Q flows from the battery to charge the capacitor fully. If C = 20 μF, R = 10 ? and the battery
is ideal with emf of 50 V, identify the correct statement(s).
current I(t) = I0 cos (ωt), with I0 = 1A and ω = 500 rad/s starts flowing in it with the initial direction shown
in the figure. At
total charge Q flows from the battery to charge the capacitor fully. If C = 20 μF, R = 10 ? and the battery
is ideal with emf of 50 V, identify the correct statement(s).
A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K between its plates that
covers 1/3 of the area of its plates, as shown in the figure. The total capacitance of the
capacitor is C while that of the portion with dielectric in between is C1. When the capacitor is
charged, the plate area covered by the dielectric gets charge Q1 and the rest of the area gets
charge Q2. The electric field in the dielectric is E1 and that in the other portion is E2. Choose
the correct option/options, ignoring edge effects.
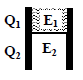
covers 1/3 of the area of its plates, as shown in the figure. The total capacitance of the
capacitor is C while that of the portion with dielectric in between is C1. When the capacitor is
charged, the plate area covered by the dielectric gets charge Q1 and the rest of the area gets
charge Q2. The electric field in the dielectric is E1 and that in the other portion is E2. Choose
the correct option/options, ignoring edge effects.
One end of a taut string of length 3m along the x axis is fixed at x = 0. The speed of the waves in the string
is 100 ms-1. The other end of the string is vibrating in the y direction so that stationary waves are set up in
the string. The possible waveform(s) of these stationary waves is (are)
A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index n1 = 1.4 is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index n2 = 1.5, as shown in the figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distance f2 from the film. Then
Heater of an electric kettle is made of a wire of length L and diameter d. It takes 4 minutes to raise the
temperature of 0.5 kg water by 40 K. This heater is replaced by a new heater having two wires of the same
material, each of length L and diameter 2d. The way these wires are connected is given in the options.
How much time in minutes will it take to raise the temperature of the same amount of water by 40K?
Two ideal batteries of emf V1 and V2 and three resistances R1, R2 and R3 are connected as shown in the figure. The current in resistance R2 would be zero if
Let E1 (r), E2 (r) and E3 (r) be the respective electric fields at a distance r from a point charge Q, an
infinitely long wire with constant linear charge density λ, and an infinite plane with uniform surface charge
density σ. If E1(r0 ) = E2 (r0 ) = E3 (r0 ) at a given distance r0, then
A light source, which emits two wavelengths λ1 = 400 nm and λ2 = 600 nm, is used in a Young’s double
slit experiment. If recorded fringe widths for λ1 and λ2 are β1 and β2 and the number of fringes for them
within a distance y on one side of the central maximum are m1 and m2, respectively, then
In the figure, a ladder of mass m is shown leaning against a wall. It is in static equilibrium making an angle
θ with the horizontal floor. The coefficient of friction between the wall and the ladder is μ1 and that
between the floor and the ladder is μ2. The normal reaction of the wall on the ladder is N1 and that of the
floor is N2. If the ladder is about to slip, then
Q. No. 11 - 20 carry 3 Marks each
Each question, when worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
During Searle’s experiment, zero of the Vernier scale lies between 3.20 x 10-2 m and 3.25 x 10-2 m of the
main scale. The 20th division of the Vernier scale exactly coincides with one of the main scale divisions.
When an additional load of 2 kg is applied to the wire, the zero of the Vernier scale still lies between 3.20 x
10-2 m and 3.25 x10-2 m of the main scale but now the 45th division of Vernier scale coincides with one of
the main scale divisions. The length of the thin metallic wire is 2 m and its cross-sectional area is 8 x 10-7
m2. The least count of the Vernier scale is 1.0 x 10-5 m. The maximum percentage error in the Young’s
modulus of the wire is
Airplanes A and B are flying with constant velocity in the same vertical plane at angles 300 and 600 with
respect to the horizontal respectively as shown in the figure. The speed of A is 100√3 ms-1. At time t = 0
s, an observer in A finds B at a distance of 500 m. This observer sees B moving with a constant velocity
perpendicular to the line of motion of A. If at t = t0, A just escapes being hit by B, t0 in seconds is
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state i with internal energy Ui = 100 J to the final state f
along two different paths iaf and ibf, as schematically shown in the figure. The work done by the system
along the paths af, ib and bf are Waf = 200 J, Wib = 50 J and Wbf = 100 J respectively. The heat supplied to
the system along the path iaf, ib and bf are iaf ib Q , Q and Qbf respectively. If the internal energy of the
system in the state b is Ub = 200 J and Qiaf = 500 J, the ratio Qbf / Qib is
Two parallel wires in the plane of the paper are distance X0 apart. A point charge is moving with speed u
between the wires in the same plane at a distance X1 from one of the wires. When the wires carry current of
magnitude I in the same direction, the radius of curvature of the path of the point charge is R1. In contrast,
if the currents I in the two wires have directions opposite to each other, the radius of curvature of the path is R2. id X0/X1 =3 the value of R1/ R2 is
To find the distance d over which a signal can be seen clearly in foggy conditions, a railways engineer uses
dimensional analysis and assumes that the distance depends on the mass density ρ of the fog, intensity
(power/area) S of the light from the signal and its frequency f. The engineer finds that d is proportional to
S1/n. The value of n is
A rocket is moving in a gravity free space with a constant acceleration of 2 ms–2 along + x direction (see figure). The length of a chamber inside the rocket is 4 m. A ball is thrown from the left end of the chamber in + x direction with a speed of 0.3 ms–1 relative to the rocket. At the same time, another ball is thrown in +x direction with a speed of 0.2 ms–1 from its right end relative to the rocket. The time in seconds when the two balls hit each other is
A galvanometer gives full scale deflection with 0.006 A current. By connecting it to a 4990 resistance, it can be converted into a voltmeter of range 0 – 30 V. If connected to a 2n/249
resistance, it becomes an ammeter of range 0 – 1.5 A. The value of n is
A uniform circular disc of mass 1.5 kg and radius 0.5 m isinitially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. Three forces of equal magnitude F = 0.5 N are applied simultaneously along the three sides of an equilateral
triangle XYZ with its vertices on the perimeter of the disc (see figure). One second after applying the forces, the angular speed of the disc in rad s–1 is
A horizontal circular platform of radius 0.5 m and mass 0.45 kg is free to rotate about its axis. Two massless spring toy-guns, each carrying a steel ball of mass 0.05 kg are attached to the platform at a distance 0.25 m from the centre on its either sides along its diameter (see figure). Each gun simultaneously fires the balls horizontally and perpendicular to the diameter in opposite directions. After leaving the platform, the balls have horizontal speed of 9 ms–1 with respect to the ground. The rotational speed of the platform in rad s–1 after the balls leave the platform is
Consider an elliptically shaped rail PQ in the vertical plane with OP = 3 m and OQ = 4 m. A block of mass 1 kg is pulled along the rail from P to Q with a force of 18 N, which is always parallel to line PQ (see the figure given). Assuming no frictional losses, the kinetic energy of the block when it reaches Q is (n×10) Joules. The
value of n is (take acceleration due to gravity = 10 ms–2)
Q. No. 21- 30 carry 3 mark each.
Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. The correct combination of names for isomeric alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O is/are
An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure = P1, volume = V1 and absolute
temperature = T1 expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final
internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are P2, V2 and T2, respectively. For this
expansion,
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomena:
For the reaction:
The correct statement(s) in the balanced equation is/are:
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below:
The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained by
The correct statement(s) for orthoboric acid is/are
Upon heating with Cu2S, the reagent(s) that give copper metal is/are
The pair(s) of reagents that yield paramagnetic species is/are
In the reaction shown below, the major product(s) formed is/are
|
3 videos|2 docs|40 tests
|
|
3 videos|2 docs|40 tests
|


















