JEE Advanced 2014 Paper -2 with Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test National Level Test Series for JEE Advanced 2025 - JEE Advanced 2014 Paper -2 with Solutions
A glass capillary tube is of the shape of truncated cone with an apex angle α so that its two ends have cross
sections of different radii. When dipped in water vertically, water rises in it to a height h, where the radius
of its cross section is b. If the surface tension of water is S, its density is ρ, and its contact angle with glass
is θ, the value of h will be (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
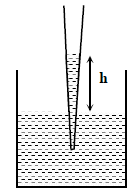
sections of different radii. When dipped in water vertically, water rises in it to a height h, where the radius
of its cross section is b. If the surface tension of water is S, its density is ρ, and its contact angle with glass
is θ, the value of h will be (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
If λcu is the wavelength of Kα X-ray line of copper (atomic number 29) and λMo is the wavelength of the K?
X-ray line of molybdenum (atomic number 42), then the ratio λcu/λMo is close to
X-ray line of molybdenum (atomic number 42), then the ratio λcu/λMo is close to
A planet of radius R = 1/10 x (radius of Earth) has the same mass density as Earth. Scientists dig a well of
depth R/5 on it and lower a wire of the same length and of linear mass density 10-3 kgm-1 into it. If the wire
is not touching anywhere, the force applied at the top of the wire by a person holding it in place is (take the
radius of Earth = 6 x 106 m and the acceleration due to gravity of Earth is 10 ms-2)
depth R/5 on it and lower a wire of the same length and of linear mass density 10-3 kgm-1 into it. If the wire
is not touching anywhere, the force applied at the top of the wire by a person holding it in place is (take the
radius of Earth = 6 x 106 m and the acceleration due to gravity of Earth is 10 ms-2)
A tennis ball is dropped on a horizontal smooth surface. It bounces back to its original position after hitting
the surface. The force on the ball during the collision is proportional to the length of compression of the
ball. Which one of the following sketches describes the variation of its kinetic energy K with time t most
appropriately? The figures are only illustrative and not to the scale.
A metal surface is illuminated by light of two different wavelengths 248 nm and 310 nm. The maximum
speeds of the photoelectrons corresponding to these wavelengths are u1 and u2, respectively. If the ratio
u1 : u2 = 2 : 1 and hc = 1240 eV nm, the work function of the metal is nearly
A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the form of quarter of a circle. The wire is
fixed vertically on ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire and it
slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from A to B, the force it applies on the wire is
During an experiment with a metre bridge, the galvanometer shows a null point when the jockey is pressed
at 40.0 cm using a standard resistance of 90 , as shown in the figure. The least count of the scale used in
the metre bridge is 1 mm. The unknown resistance is
Parallel rays of light of intensity I = 912 Wm–2 are incident on a spherical black body kept in surroundings
of temperature 300 K. Take Stefan-Boltzmann constant σ = 5.7×10–8 Wm–2 K–4 and assume that the energy
exchange with the surroundings is only through radiation. The final steady state temperature of the black
body is close to
A point source S is placed at the bottom of a transparent block of height 10 mm and refractive index 2.72. It is immersed in a lower refractive index liquid as shown in the figure. It is found that the light emerging from the block to the liquid forms a circular bright spot of diameter 11.54 mm on the top of the block. The refractive index of the liquid is
Q.No. 11 - 16 carry 3 marks each
This section contains 3 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. Six questions relate to the three paragraphs with two questions on each paragraph. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Paragraph For Questions 11 & 12
The figure shows a circular loop of radius a with two long parallel wires (numbered 1 and 2) all in the plane of the paper. The distance of each wire from the centre of the loop is d. The loop and the wires are carrying the same current I. The current in the loop is in the counterclockwise direction if seen from above.
Q.
When d ≈ a but wires are not touching the loop, it is found that the net magnetic field on the axis of the
loop is zero at a height h above the loop. In that case
Paragraph
The figure shows a circular loop of radius a with two long parallel wires (numbered 1 and 2) all in the plane of the paper. The distance of each wire from the centre of the loop is d. The loop and the wires are carrying the same current I. The current in the loop is in the counterclockwise direction if seen from above.
Q.
Consider d >> a, and the loop is rotated about its diameter parallel to the wires by 30° from the position
shown in the figure. If the currents in the wires are in the opposite directions, the torque on the loop at its
new position will be (assume that the net field due to the wires is constant over the loop)
Paragraph for Questions 13 & 14
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container and
the piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside and
inside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of a
thermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container
is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2
moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas are and those for an ideal diatomic gas are
Q.
Consider the partition to be rigidly fixed so that it does not move. When equilibrium is achieved, the final
temperature of the gases will be
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container and
the piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside and
inside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of a
thermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas are and those for an ideal diatomic gas are
Q.
Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in both
compartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will be
Paragraph for Questions 15 & 16
A spray gun is shown in the figure where a piston pushes air out of a nozzle. A thin tube of uniform cross section is connected to the nozzle. The other end of the tube is in a small liquid container. As the piston
pushes air through the nozzle, the liquid from the container rises into the nozzle and is sprayed out. For the spray gun shown, the radii of the piston and the nozzle are 20 mm and 1 mm respectively. The upper end of the container is open to the atmosphere.
Q.
If the piston is pushed at a speed of 5 mms–1, the air comes out of the nozzle with a speed of
If the density of air is ρa and that of the liquid ρl , then for a given piston speed the rate (volume per unit
time) at which the liquid is sprayed will be proportional to
Q. no 17-21 cary 3 marks each.
Each queation having two matching lists. Choices for the correct combination of elements from List-I and List-II are given as option (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which one is correct.
Q.
A person in a lift is holding a water jar, which has a small hole at the lower end of its side. When the lift is at rest, the water jet coming out of the hole hits the floor of the lift at a distance d of 1.2 m from the person. In the following, state of the lift’s motion is given in List I and the distance where the water jet hits the floor of the lift is given in List II. Match the statements from List I with those in List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
Four charges Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 of same magnitude are fixed along the x axis at x = -2a, -a, +a and +2a,
respectively. A positive charge q is placed on the positive y axis at a distance b > 0. Four options of the
signs of these charges are given in List I. The direction of the forces on the charge q is given in List II.
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
Four combinations of two thin lenses are given in List I. The radius of curvature of all curved surfaces is r
and the refractive index of all the lenses is 1.5. Match lens combinations in List I with their focal length in
List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
A block of mass m1 = 1 kg another mass m2 = 2kg, are placed together (see figure) on an inclined plane
with angle of inclination θ. Various values of θ are given in List I. The coefficient of friction between the
block m1 and the plane is always zero. The coefficient of static and dynamic friction between the block m2
and the plane are equal to μ = 0.3. In List II expressions for the friction on the block m2 are given. Match
the correct expression of the friction in List II with the angles given in List I, and choose the correct option.
The acceleration due to gravity is denoted by g.
[Useful information: tan (5.5o) ≈ 0.1; tan (11.5o) ≈ 0.2; tan (16.5o) ≈ 0.3]
Inst.
Q. No 1- 10 carry 3 marks each and 1 as negative marking for incorrect answer
Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
Charges Q, 2Q and 4Q are uniformly distributed in three dielectric solid spheres 1, 2 and 3 of radii R/2, R
and 2R respectively, as shown in figure. If magnitudes of the electric fields at point P at a distance R from
the centre of spheres 1, 2 and 3 are E1, E2 and E3 respectively, then
Q. No 21- 40 carry 3 marks each and 1 as negative marking for incorrect answer
Q.
Assuming 2s – 2p mixing is NOT operative, the paramagnetic species among the following is
For the process
at T = 100oC and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is
For the elementary reaction M → N, the rate of disappearance of M increases by a factor of 8 upon
doubling the concentration of M. The order of the reaction with respect to M is
For the identification of β-naphthol using dye test, it is necessary to use
Isomers of hexane, based on their branching, can be divided into three distinct classes as shown in the
figure.
The correct order of their boiling point is
The major product in the following reaction is
[Figure
Under ambient conditions, the total number of gases released as products in the final step of the reaction
scheme shown below is
The product formed in the reaction of SOCl2 with white phosphorous is
Hydrogen peroxide in its reaction with KIO4 and NH2OH respectively, is acting as a
The acidic hydrolysis of ether (X) shown below is fastest when
Figure
|
3 videos|3 docs|40 tests
|
|
3 videos|3 docs|40 tests
|


















