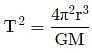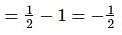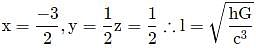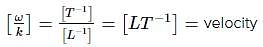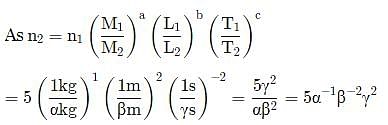Test: Dimensional analysis and its applications (April 3) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Dimensional analysis and its applications (April 3)
Using the principle of homogeneity of dimensions, which of the following is correct?
If the energy, E = Gp hq cr where G is the universal gravitational constant, h is the Planck's constant and c is the velocity of light, then the values o f p, q and r are, respectively
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following relations is dimensionally incorrect?
If velocity of light c, Planck's constant h and gravitational constant G are taken as fundamental quantities then the dimensions of length will be:
The equation of state of a gas is given by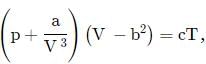 where p,V,T are pressure, volume and temperature respectively and a,b,c are constants. The dimensions of a and b are respectively
where p,V,T are pressure, volume and temperature respectively and a,b,c are constants. The dimensions of a and b are respectively
The displacement of a progressive wave is represented by y = A sin(ωt - kx) where x is distance and t is time. The dimensions of ω/k are same as those of the
Which of the following relations for the displacement of a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion is not correct dimensionally?
A new system of units is proposed in which unit of mass is α kg, unit of length is β m and unit of time is γ s. What will be value of 5 J in this new system?
The velocity of a particle (v) at an instant t is given by v = at + bt2. The dimension of b is the
Checking the correctness of equations using the method of dimensions is based on
|
360 tests
|