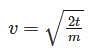Test: Introduction to work and energy & Kinetic Energy (June 21) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Introduction to work and energy & Kinetic Energy (June 21)
Two masses of 1 g and 4g are moving with equal kinetic energy. The ratio of the magnitudes of their momenta is
At time t = 0 s particle starts moving along the x-axis. If its kinetic energy increases uniformly with time ‘t’, the net force acting on it must be proportional to
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Time rate at which work is done by a force is:
There are two bodies X and Y with equal kinetic energy but different masses m and 4m respectively. The ratio of their linear momentum is:
Find the potential energy stored in a ball of mass 5 kg placed at a height of 3 m above the ground.
Output of a truck is 4500 J and its efficiency is 50%, the input energy provided to the truck is:
By how much does kinetic energy increase if the momentum is increased by 20%?
When a body slides against a rough horizontal surface, the work done by friction is:
A machine gun fires 60 bullets per minute, with a velocity of 700 m/s. If each bullet has a mass of 50g, find the power developed by the gun.
If a force acts perpendicular to the direction of motion of a body, what is the amount of work done?
|
360 tests
|