Test: Newton's laws of Motion (June 2) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Newton's laws of Motion (June 2)
A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius 1.5 m with a speed of 40 rev./min in a horizontal plane. The speed is then increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks.
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s−1, what would be the reading on the scale?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
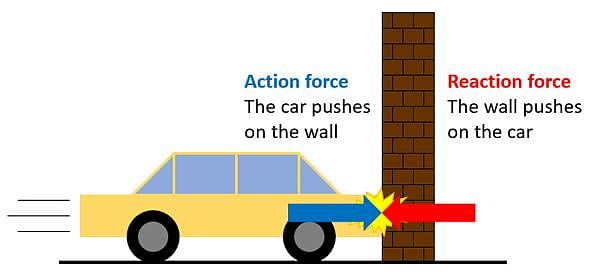
Newton’s third law states that when two bodies interact.
According to Newton's third law of motion, the action and reaction forces are
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass 0.1 kg lying on the floor of a train which is accelerating with 1 ms−2, the stone being at rest relative to the train. Neglect air resistance.
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform acceleration of 10 ms−2 what would be the reading on the scale?
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 ms−2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
|
360 tests
|