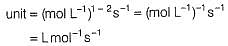Test: Rate of a Chemical Reaction and factors influencing rate of reaction(6 Nov) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Rate of a Chemical Reaction and factors influencing rate of reaction(6 Nov)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
For a given reaction,
A → Product,
rate = 1 x 10-4 Ms-1 at [A] = 0.01 M
rate = 1.41 x 10-4 Ms-1 at [A] = 0.02 M
Hence, rate law is
rate = 1.41 x 10-4 Ms-1 at [A] = 0.02 M
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given by
rate = k[A]n [B]m
If concentration of A is doubled and that of B is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The rate equation for the reaction,
2A + B → C
is found to be, rate = k[A] [B]
Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
For the reaction,
2 A+B → Product
The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is
Which of the following statements appears to the first order reaction?
2N2O5(CCl4) → 4NO2(CCl4) + O2(g)
For a reaction, time of 75% reaction is thrice of time of 50% reaction. Thus, order of the reaction is
For nth order reaction,
Graphs between log (rate) and log[A0] are of the type ([A0] is the initial concentration)
Lines P, Q, R and S are for the order
nA → Product
For the reaction, rate constant and rate of the reaction are equal, then on doubling the concentration of A, rate becomes,
For the simple reaction,
A → B
When [A] was changed from 0.502 mol dm-3 to 1.004 mol dm-3 half-life dropped from 52 s to 26 s at 300 K. Thus, order of the reaction is
For the following reaction,
Variation of T50 with [A] is shown
Q.
After 10 min volume of N2 (g) is 10 L and after complete reaction, volume of N2 (g) is 50 L. Thus, T50 is
|
360 tests
|