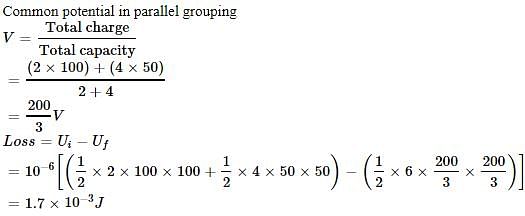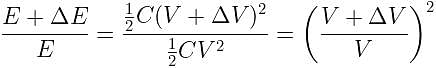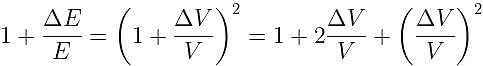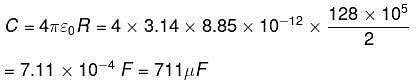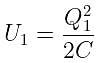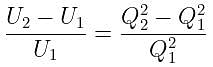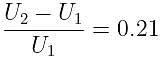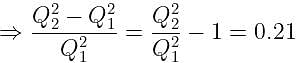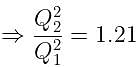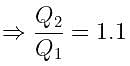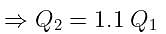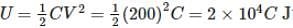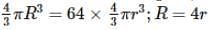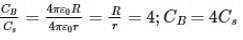Test: Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance(5 Nov) - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance(5 Nov)
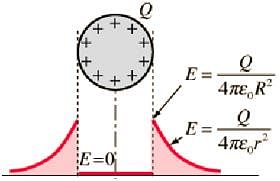
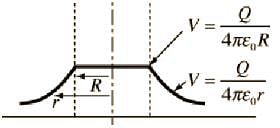
For a charged conductor of arbitrary shape, inside the conductor
An equipotential surface is a surface ______.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A variable capacitor and an electroscope are connected in parallel to a battery. The reading of the electroscope would be decreased by_______
A 2μF capacitor C1 is charged to a voltage 100 V and a 4 μF capacitor C2 is charged to a voltage 50 V. The capacitors are then connected in parallel. What is the loss of energy due to parallel connection?
If the potential difference between the plates of a capacitor is increased by 0.1%, the energy stored in the capacitor increases by nearly:
If the diameter of earth is 128 x 102 km, then its capacitance will be:
If a charge moves in an electrical field:
If the charge on a capacitor is increased by 2 coulomb, the energy stored in it increases by 21%. The original charge on the capacitor (in coulomb) is:
In series combination of capacitors, potential drops across the individual capacitors are equal to_______
A capacitor of capacitance C is fully charged by a 200 V supply. It is then discharged through a small coil of resistance wire embedded in a thermally insulated block of specific heat 2.5×102Jkg−1K−1 and of mass 0.1 kg. If the temperature of the block rises by 0.4 K, what is the value of C?
64 water drops having equal charges combine to form one bigger drop. The capacitance of the bigger drop, as compared to that of smaller drop will be:
An electrolytic capacitor is marked 8 μF, 220 V. It can be used in a circuit where the p.d. across the capacitor may be:
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is 5 μF. When a glass slab of thickness equal to the separation between the plates is introduced between the plates, the potential difference reduces to 1/8 of the original value. The dielectric constant of glass is
For a parallel plate capacitor ______________ possible potential difference between the capacitor plates.
Which of the following is true about equipotential lines?
|
360 tests
|