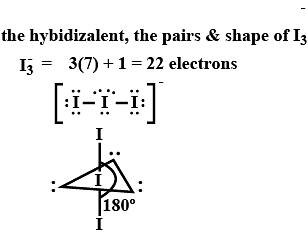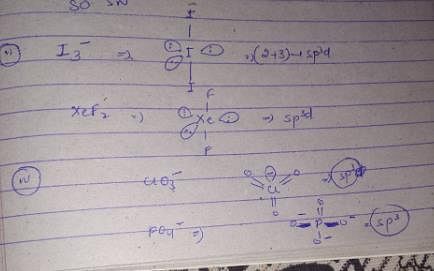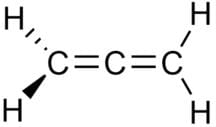Test: Chemical Bonding- 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Inorganic Chemistry - Test: Chemical Bonding- 1
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
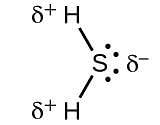
Which of the following is the electron-deficient molecule?
If a bond is made up of a large number of organic compound, then the bond is termed as ______.
The hybridization, lone pair of electrons, and shape of I3− is:
Which compound species has all the carbons, with same kind of hybridization?
Which among the following formation is not an example of Covalent bond?
Which type of bond will be formed by overlapping of dxz and dxz orbitals if the molecular axis is x-axis?
In which of the following processes, the bond order has increased and paramagnetic character has changed to diamagnetic?
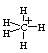
The hybridization state in triangular bipyramidal CH5+ is:
Which among the following chemical bond were described by Kossel and Lewis?
The percentage of p-character in the orbitals forming P−P bonds in P4 is
The hybridization state in ‘B’ when BF3 form adduct with ether is:
In which of the following pairs, both the species have the same hybridisation?
(I) SF4,XeF4 (II) I−3,XeF2 (III) ICl+4,SiCl4 (IV) ClO−3,PO3−4
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are):
With respect to hyper valence theory, which will have multicenter bonding:
Which of the following are isoelectronic and isostructural NO3−, CO3−2, ClO3−, SO3
|
48 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|