Test: Aromaticity & Acid Base Properties - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Aromaticity & Acid Base Properties
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c), and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
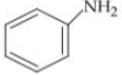
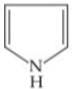
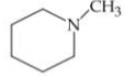
Q. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their basic strength.
1.
2.
3.
4.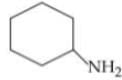




In the compound below, which nitrogen is protonated first when treated with HCI?
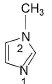
Which of the following compounds is more easily oxidised to a carbonyl when treated with MnO2?
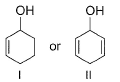
Which among these is the simplest example for polycyclic arenes?
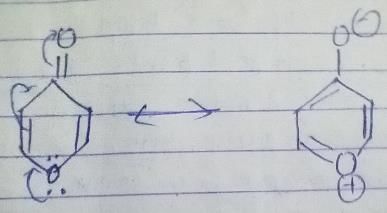
The compound shown below evolve hydrogen gas when refluxed with potassium metal, why?
Which compound below has maximum tendency to form a salt when treated with HBr?
What is the correct order of increasing acidic strength of the following?
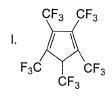
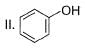
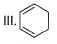
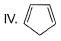
How many Kekule structures exist for benzene?
How many monobromo derivatives exists for anthracene?
7-bromo-1,3,5-cycloheptatriene exists as ionic species in aqueous solution while 5-bromo-1,3-cyclopentadiene does not ionise even in presence of AgNO3(aq) because
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Consider the following compounds.
The correct statement regarding properties of above mentioned compounds is/are
Which of the following systems are aromatic?
What is true about the 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene?
What is true regarding the following compound?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
|
119 videos|338 docs|74 tests
|