Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
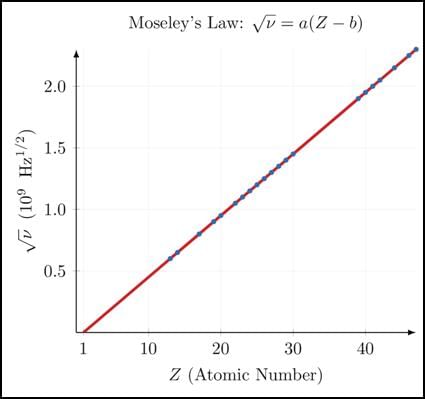
According to Moseley, a straight-line graph is obtained on plotting-
Moseley performed experiments and studied the frequencies of which radiations emitted from the elements?
Among the following statements the one that is not true about Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is:
Which scientist proposed that atomic number is more fundamental property of an element than its atomic mass?
Johann Dobereiner classified elements in group of three elements called as:
In the modern periodic table, which period contains 32 elements?
Horizontal rows in the periodic table are called:
The third period of the modern periodic table contains
Newland arranged elements in increasing order of atomic weights and noted that every eighth element had properties similar to:
Which of the following sets of elements was part of Döbereiner's Triads?
Lothar Meyer proposed that on arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic weights; similarities appear in which type of properties?
Eka silicon predicted by Mendeleev is which element:
Eka aluminium predicted by Mendeleev is which element?
In Dobereiner's Triads, elements were grouped based on their similar chemical properties. Which of the following elements was not part of any known Dobereiner's Triad?
The basis of long form of periodic table is:
Newland's Law of Octaves suggested that elements exhibited similar properties at regular intervals. However, this law failed to accommodate the discovery of:
Mendeleev predicted the existence of which element/elements in the periodic table?
Mendeleev's Periodic Table was arranged primarily based on which property of elements?
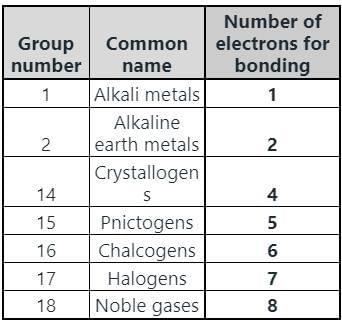
In which group of the modern periodic table are halogens placed?
Chalcogens belong to which group of the periodic table?