Case Based Questions Test: Equilibrium - NEET MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Case Based Questions Test: Equilibrium
The variables Pressure, Volume, Concentration and Temperature may change the State of Equilibrium. The change is governed by the Le-Chatelier’s principle. The decomposition of NH3(g) can be made spontaneous by increasing the temperature and lowering pressure. In the reaction, removal of any product from the reaction mixture makes the reversible reaction irreversible and therefore, reaction proceeds to completion. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. The equilibrium Solid → Liquid → Gas will shift in forward direction when:
The variables Pressure, Volume, Concentration and Temperature may change the State of Equilibrium. The change is governed by the Le-Chatelier’s principle. The decomposition of NH3(g) can be made spontaneous by increasing the temperature and lowering pressure. In the reaction, removal of any product from the reaction mixture makes the reversible reaction irreversible and therefore, reaction proceeds to completion. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. At 25°C, the equilibrium constant K1 and K2 are for the reactions:
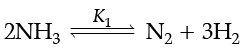
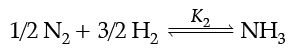
Which of the following shows the relation between two equilibrium constants?
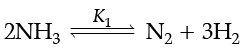
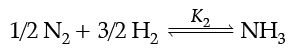
The variables Pressure, Volume, Concentration and Temperature may change the State of Equilibrium. The change is governed by the Le-Chatelier’s principle. The decomposition of NH3(g) can be made spontaneous by increasing the temperature and lowering pressure. In the reaction, removal of any product from the reaction mixture makes the reversible reaction irreversible and therefore, reaction proceeds to completion. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour at its boiling point. On an average, the molecules in the two phases have equal:
The variables Pressure, Volume, Concentration and Temperature may change the State of Equilibrium. The change is governed by the Le-Chatelier’s principle. The decomposition of NH3(g) can be made spontaneous by increasing the temperature and lowering pressure. In the reaction, removal of any product from the reaction mixture makes the reversible reaction irreversible and therefore, reaction proceeds to completion. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. Change in free energy for the equilibrium, gaseous reaction, PCl5 → PCl3 + Cl2 on addition of an inert gas at constant pressure and at constant volume is respectively:
Greater the degree of dissociation (a) of an acid or base, greater is its acidic or basic strength. The relative strengths of weak acids or bases are compared in terms of √Ka or √Kb.
Weak electrolytes are dissociated to less extent in water. Dissociation constants depend upon temperature.
The questions given (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) reason (R). Choose the correct option.
Assertion: The dissociation constants of polybasic acids are in the order K1 > K2 > K3.
Reason: The [H+] in first step of dissociation exerts common ion effect to decrease the second dissociation.
Greater the degree of dissociation (a) of an acid or base, greater is its acidic or basic strength. The relative strengths of weak acids or bases are compared in terms of √Ka or √Kb.
Weak electrolytes are dissociated to less extent in water. Dissociation constants depend upon temperature.
The questions given (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) reason (R). Choose the correct option.
Assertion: The equilibrium constant is fixed and is a characteristic of any given chemical reaction at a specified temperature.
Reason: The composition of the final equilibrium mixture at a particular temperature depends upon the starting amount of reactants.
Greater the degree of dissociation (a) of an acid or base, greater is its acidic or basic strength. The relative strengths of weak acids or bases are compared in terms of √Ka or √Kb.
Weak electrolytes are dissociated to less extent in water. Dissociation constants depend upon temperature.
The questions given (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) reason (R). Choose the correct option.
Assertion: The ionisation of Hydrogen Sulphide in water is low in the presence of Hydrochloric acid.
Reason: Hydrogen Sulphide is a weak acid.
Greater the degree of dissociation (a) of an acid or base, greater is its acidic or basic strength. The relative strengths of weak acids or bases are compared in terms of √Ka or √Kb.
Weak electrolytes are dissociated to less extent in water. Dissociation constants depend upon temperature.
The questions given (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) reason (R). Choose the correct option.
Assertion: When dilution increases, the degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte also increases.
Reason: The degree of dissociation is inversely proportional to concentration. When the dilution increases by 100 times, the dissociation increases by 10 times.
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|