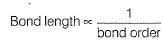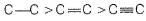Test: Covalent & Coordinate Bonding - NEET MCQ
28 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Covalent & Coordinate Bonding
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. By Lewis structure NO has following fact
Based on valence bond theory, types of bonding in H2O are
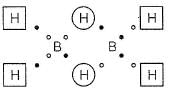
Bond order of (B— H) x and y bonds in diborane are respectively
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis, which out of the following will not form sigma bond.
In which of the following molecules would you expect the N to N bond to be shortest ?
Which of these molecules have non-bonding electron pairs on the central atom?
I. SF4
II. ICI3
III. SO2
IV. NH3
V. SiF4
When a chemical bond is formed, there is decrease in
Mean bond enthalpy of different bonds are given
Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
Q. Which of the following species contain at least one atom that violates the octet rule?
Which of the following is/are correct statement(s)?
Electron-seeking species are called electrophiles. Which of the following sets consists of electrophiles only?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-25) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)
Graph shows variation of percentage ionic character with (EN) difference of two elements.
Q. Which of the following bonds is most polar?
Which of the following option with respect to the Pauling electronegativity values of the element is
Passage II
Consider the following structure
Q. Shortest (C— H) bond is
Passage II
Consider the following structure
Q. Shortest (carbon-carbon) bond is
Which among the following chemical bond were described by Kossel and Lewis?
Direction (Q. Nos. 26) Choice for the correct combination of elements from coloumn I and Coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Match the species in Column I with their properties in Column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 27 and 28) This section contains 2 question. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. In acidic medium,H2O2 changes Cr2O72- to CrO5 which has two (-O-O-) bonds. Oxidation state of Cr in CrO3 is
K2Cr2O7 is an oxidising agent in acidic medium. How many O-atoms are directly linked to each Cr-atom?
|
127 videos|245 docs|87 tests
|