Assertion & Reason Test: Redox Reactions - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Assertion & Reason Test: Redox Reactions
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion(A): Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
Assertion(A): Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason (R) : Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): In the reaction between potassium permanganate and potassium iodide, permanganate ions act as oxidising agent.
Reason (R) : Oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7 during the reaction.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): In the reaction between potassium permanganate and potassium iodide, permanganate ions act as oxidising agent.
Reason (R) : Oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7 during
the reaction.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen is an example of disproportionation reaction.
Reason (R) : The oxygen of peroxide is in –1 oxidation state and it is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 and – 2 oxidation state in H2O.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen is an example of disproportionation reaction.
Reason (R) : The oxygen of peroxide is in –1 oxidation state and it is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 and –2 oxidation state in H2O.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Redox couple is the combination of oxidised and reduced form of a substance involved in an oxidation or reduction half cell.
Reason (R) : In the representation ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() are redox couples.
are redox couples.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): Structure I is more accurate than II

Reason (R): More electronegative oxygen atom carries negative charge in I.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Redox couple is the combination of oxidised and reduced form of a substance involved in an oxidation or reduction half cell.
Reason (R) : In the representation EOFe3+ /Fe2+ and EO Cu2+/Cu, Fe3+/ Fe2+ and Cu2+ / Cu are redox couples.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
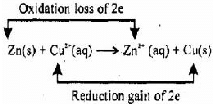
Assertion (A) : In a reaction Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Zn is a reductant but itself get oxidized.
Reason (R) : In a redox reaction, oxidant is reduced by accepting electrons and reductant is oxidized by losing electrons.
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|