R.C. Mukherjee Test: Thermodynamics - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - R.C. Mukherjee Test: Thermodynamics
If Vf is the final volume and Vi is the initial volume and pex the external pressure the work done can be calculated by
Spontaneity in the context of chemical thermodynamics means
Enthalpy of combustion of carbon to CO2is –393.5 kJ mol−1. Calculate the heat released upon formation of 35.2 g of CO2from carbon and dioxygen gas.
The volume of gas is reduced to half from its original volume. The specific heat will
A cylinder confines 2.00 L gas under a pressure of 1.00 atm. The external pressure is also 1.00 atm. The gas is heated slowly, with the piston sliding freely outward to maintain the pressure of the gas close to 1.00 atm. Suppose the heating continues until a final volume of 3.50 L is reached. Calculate the work done on the gas.
A spherical constant temperature heat source of radius r1 is at the center of a uniform solid sphere of radius r2. The rate at which heat is transferred through the surface of the sphere is proportional to
For a process from state 1 to state 2, heat transfer in a reversible process is given by
Suppose a 10.00-kg mass drops through a height difference of 3.00 m, and the resulting work is used to turn a paddle in 200.0 g water, initially at 15.00∘C. The final water temperature is found to be 15.35∘C. Assuming that the work done is used entirely to increase the water temperature, calculate the conversion factor between joules and calories.
The molar heat capacity of a substance is the
If change in Gibbs energy ΔG is negative (< 0)
Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CH3OH(l) from the following data:
CH3OH(I)+3/2O2(g)→CO2(g)+2H2O(l); △rHθ=−726kJmol−1
C(graphite)+O2(g)→CO2(g); △cHθ=−393kJmol−1
H2(g)+1/2O2(g)→H2O(l); △fHθ=−286kJmol−1
During complete combustion of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of heat is released. The thermochemical reaction for above change is ΔfU0 of formation of CH4 (g) at certain temperature is –393 kJ mol−1. The value of ΔfH0is
In an adiabatic process, no transfer of heat takes place between system and surroundings. Choose the correct option for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition from the following.
The relationship between Cp and CV for an ideal gas is
A thermodynamic state function is a physical quantity
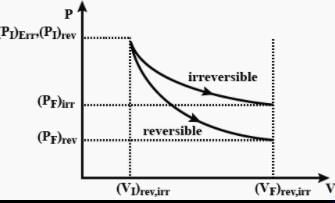
The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using the expression The work can also be calculated from the pV– plot by using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed (a) reversibly or (b) irreversibly from volume Vi to Vf . choose the correct option.
Suppose that 1.00 kJ of heat is transferred to 2.00 mol argon (at 298 K, 1 atm). What will the final temperature Tf be if the heat is transferred at constant volume?
For the process to occur under adiabatic conditions, the correct condition is:
For an isolated system, ΔU = 0, what will be ΔS?
The entropy change can be calculated by using the expression When water freezes in a glass beaker, choose the correct statement amongst the following :
|
127 videos|245 docs|87 tests
|