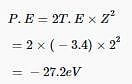Bohr's Theory Of Hydrogen Atom - NEET MCQ
19 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Bohr's Theory Of Hydrogen Atom
‘Hartree’ is the atomic unit of energy and is equal to
Wave number of a spectral line for a given transition is x cm-1 for He+, then its value for Be3+ (isoelectronic of He+)for the same transition is
Which of the following electronic transitions requires that the greatest quantity of energy be absorbed by a hydrogen atom ?
An electron in H-atom in its ground state absorbs 1.5 times as much as energy as the minimum required for its escape from the atom
Q.
Thus, kinetic energy given to the emitted electron is
Ionisation energy of He+ is 19.6x10-18 J atom -1. The energy of the first stationary state (n = 1)of Li2+ is
The kinetic energy of an electron in the second Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom is (a0 is Bohr radius)
[AIEEE 2012]
Energy of the electron in nth orbit is given by E Wavelength of light required to excite an electron in an H-atom from level n = 1 to n = 2 will be (h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s ; c = 3.0 x 108ms -1)
[AIEEE 2012]
The potential energy of an electron in the second Bohr's orbit of the he±
In Lyman series, shortest wavelength of H-atom appears at x m, then longest wavelength in Balmer series of He+ appear at
If the radius of the first Bohr orbit is x, then de-Broglie wavelength of the electron in the third orbit is nearly
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
Radius of Bohr’s orbit of H-atom is 52.9 pm. An emission in H-atom starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm.
Q.
Wavelength (in nm) associated with this emission is
Radius of Bohr’s orbit of H-atom is 52.9 pm. An emission in H-atom starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm.
Q. Spectral line appears in .......... region.
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q.
Match the equation in Column I with the name type in Column II.
lf En = total energy, Kn = kinetic energy, Vn = potential energy and rn = radius of the nth orbit, then based on Bohr’s theory, match the parameter in Column I with the values in Column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 19) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. The energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of H-atom is -13.6 eV. What is the possible value of quantum number for the excited state to have energy -3.4 eV?
An emission is Be3+ in observed at 2.116 A°. In which orbit is it placed?
At what minimum atomic number, a transition from n = 2 to n = 1 energy level results in the emission of X-rays with wavelength 3.0 x 10-8 m?
Find the number of waves made by a Bohr’s electron in one complete revolution in its 3rd orbit
|
127 videos|245 docs|87 tests
|