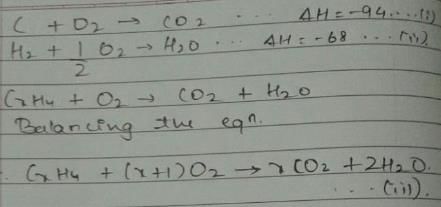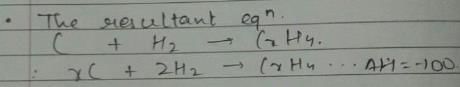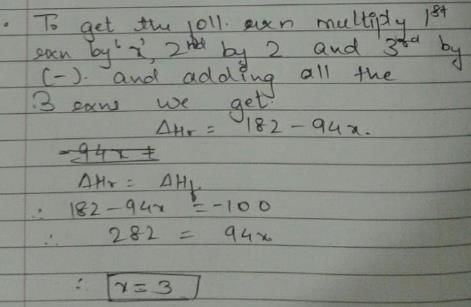Test: Hess's Law of Constant Heat Summation - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Hess's Law of Constant Heat Summation
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-7) This section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Given,
The enthalpies of elements in their standard states are taken as zero. The enthalpy of formation of a compound
Diborane is a potential rocket fuel which undergoes combustion according to the reaction,
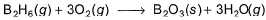
From the following data, enthalpy change for the combustion of diborane is
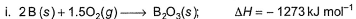
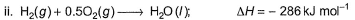

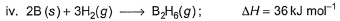
Following diagram represents Born-Haber cycle to determine lattice energy of NaCI(s). It is based on Hess’s law of constant heat summation. ΔlatticeH° of
Given, HCI (g) → H (g) + Cl (g) at 298 K (say temperature T K),
For
Q. Thus, for the given reaction (at 0 K) is
The measured enthalpy change for burning of ketene (g) (CH2CO) is - 981.1 kJ mo-1 at 298 K ,CH2CO (g)+ 2O2(g) → 2CO2 (g) + H2O (g) and that of CH4 (g) is - 802.3 kJ mol-1 at 298 K
Thus, enthalpy change at 298 K for the following thermochemical reaction is
The condition for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition is
Direction (Q. Nos. 9 and 10) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).
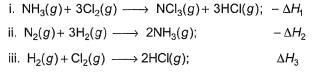
Consider the following thermochemical equations
Q. ΔrH° of the following thermochemical reaction is
CIO2 (g) + O (g) → CIO3 (g)
Consider the following thermochemical equations
Q. ΔrH° of the following thermochemical reaction is
Direction (Q. Nos. 11) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. For liquid water at
Compare the parameters ΔH1, ΔH2 ... in Column I with the corresponding values in kJ in Column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Based on (BE) values, ΔrH° of the following reaction 298 K is
Heat of combustion of CH2CO(g) is - 981.1 kJ mol-1 and that of CH4 (g) is - 802.3 kJat 298 K. If 1247.0 kJ of heat is released in the following change
Q. How many moles of CH4(g)are used?
Consider the following reactions
Q. What is the resonance energy (in kcal) of A?
Given, enthalpy of combustion of carbon (s) = -94 kcal mol-1
H2(g) = - 68 kcal mol-1 and CXH4 = - 318 kcal mol-1 and ΔfH° (CxH4) = - 100 kcal mol-1
Q. What is the value of x?
|
127 videos|245 docs|87 tests
|